Difference between revisions of "Digamma"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
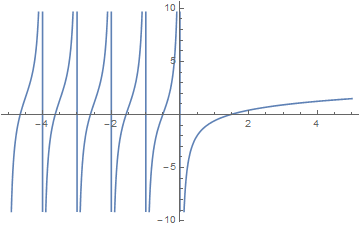
The digamma function $\psi$ is defined by | The digamma function $\psi$ is defined by | ||
| − | $$\psi(z) = \dfrac{d}{ | + | $$\psi(z) = \dfrac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d}z} \log \Gamma(z) = \dfrac{\Gamma'(z)}{\Gamma(z)}.$$ |
<div align="center"> | <div align="center"> | ||
Revision as of 18:08, 24 May 2016
The digamma function $\psi$ is defined by $$\psi(z) = \dfrac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d}z} \log \Gamma(z) = \dfrac{\Gamma'(z)}{\Gamma(z)}.$$
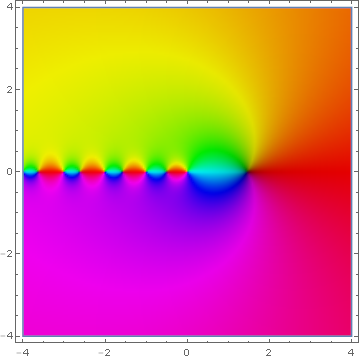
Domain coloring of analytic continuation of $\psi(z)$.
File:Domain coloring digamma.png
Properties
Theorem: $\psi(1)=-\gamma$ and for integers $n\geq 2$, $$\psi(n)=-\gamma + \displaystyle\sum_{k=1}^{n-1} \dfrac{1}{k}$$
Proof: █
Theorem: $\psi\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=-\gamma-2\log(2)$ and for integers $n \geq 1$, $$\psi \left( n + \dfrac{1}{2} \right) = -\gamma - 2 \log(2) + 2 \left( 1 + \dfrac{1}{3} + \ldots + \dfrac{1}{2n-1} \right).$$
Proof: █
Theorem: $\psi(z+1) = \psi(z) + \dfrac{1}{z}$
Proof: █
Theorem: $\psi(z+n)=\dfrac{1}{(n-1)+z} + \dfrac{1}{(n-2)+z} + \ldots + \dfrac{1}{2+z} + \dfrac{1}{1+z} + \psi(1+z)$
Proof: █
Theorem: $\psi(1-z)=\psi(z) + \pi \cot(\pi z)$
Proof: █
Theorem: $\psi(2z)=\dfrac{1}{2}\psi(z) + \dfrac{1}{2} \psi \left( z + \dfrac{1}{2} \right) + \log(2)$
Proof: █
Theorem: $\psi(\overline{z})=\overline{\psi(z)}$
Proof: █
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\dfrac{\partial}{\partial x} B(x,y)=B(x,y) \left( \dfrac{\Gamma'(x)}{\Gamma(x)} - \dfrac{\Gamma'(x+y)}{\Gamma(x+y)} \right) = B(x,y)(\psi(x) - \psi(x+y)),$$ where $B$ denotes the Beta function, $\Gamma$ denotes the gamma function, and $\psi$ denotes the digamma function.