Difference between revisions of "Error function"
(→Properties) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
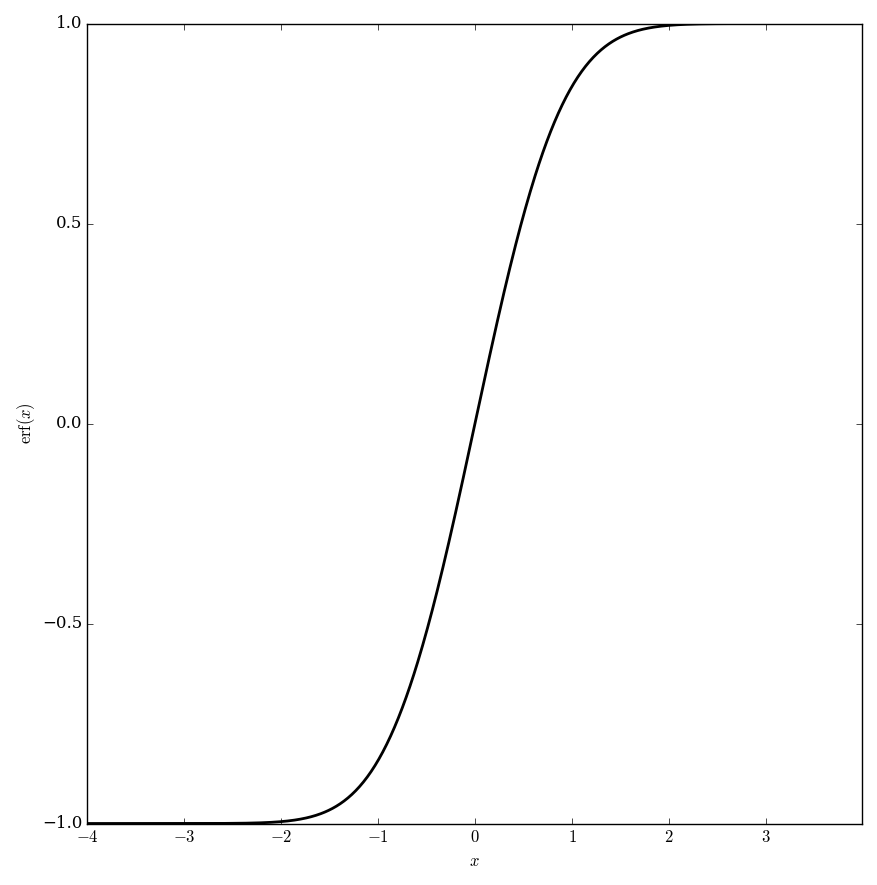
| − | The error function $\mathrm{erf}$ is defined by | + | The (normalized) error function $\mathrm{erf}$ is defined by |
| − | $$\mathrm{erf}(x)=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{\pi}}\displaystyle\int_0^x e^{-\tau^2} \mathrm{d}\tau | + | $$\mathrm{erf}(x)=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{\pi}}\displaystyle\int_0^x e^{-\tau^2} \mathrm{d}\tau,$$ |
| + | where $\pi$ denotes [[pi]] and $e^{-\tau^2}$ denotes the [[exponential]] function. | ||
<div align="center"> | <div align="center"> | ||
| Line 10: | Line 11: | ||
=Properties= | =Properties= | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[Taylor series for error function]]<br /> |
[[Series for erf with exponential factored out]]<br /> | [[Series for erf with exponential factored out]]<br /> | ||
[[Error function is odd]]<br /> | [[Error function is odd]]<br /> | ||
[[Complex conjugate of argument of error function]]<br /> | [[Complex conjugate of argument of error function]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Two-sided inequality for e^(x^2) integral from x to infinity e^(-t^2) dt for non-negative real x]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Limit of erf when z approaches infinity and the modulus of arg(z) is less than pi/4]]<br /> | ||
<div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | ||
| Line 24: | Line 27: | ||
=Videos= | =Videos= | ||
| − | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5v7d8jmlMi4 The Laplace transform of the error function $\mathrm{erf}(t)$] <br /> | + | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5v7d8jmlMi4 The Laplace transform of the error function $\mathrm{erf}(t)$ (15 September 2013)]<br /> |
| − | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CcFUQhorgdc The Error function]<br /> | + | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CcFUQhorgdc The Error function (8 November 2013)] <br /> |
| − | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1bKropXjTD0 Video 1690 - ERF Function]<br /> | + | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1bKropXjTD0 Video 1690 - ERF Function (7 July 2015)] <br /> |
=References= | =References= | ||
| + | * {{BookReference|Special Functions of Mathematical Physics and Chemistry|1956|Ian N. Sneddon|prev=Sine integral|next=findme}}: $\S 5 (5.11)$ | ||
* {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev=findme|next=Erfc}}: 7.1.1 | * {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev=findme|next=Erfc}}: 7.1.1 | ||
[http://www.johndcook.com/erf_and_normal_cdf.pdf Relating $\phi$ and erf] | [http://www.johndcook.com/erf_and_normal_cdf.pdf Relating $\phi$ and erf] | ||
| − | + | {{:Error functions footer}} | |
[[Category:SpecialFunction]] | [[Category:SpecialFunction]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:43, 25 June 2017
The (normalized) error function $\mathrm{erf}$ is defined by $$\mathrm{erf}(x)=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{\pi}}\displaystyle\int_0^x e^{-\tau^2} \mathrm{d}\tau,$$ where $\pi$ denotes pi and $e^{-\tau^2}$ denotes the exponential function.
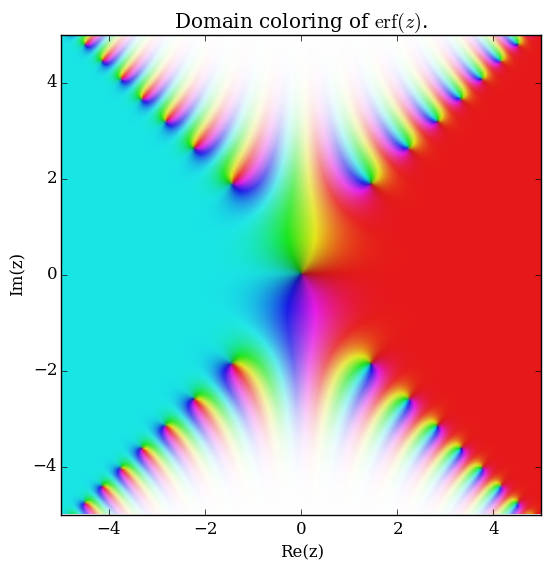
Domain coloring of $\mathrm{erf}$.
Properties
Taylor series for error function
Series for erf with exponential factored out
Error function is odd
Complex conjugate of argument of error function
Two-sided inequality for e^(x^2) integral from x to infinity e^(-t^2) dt for non-negative real x
Limit of erf when z approaches infinity and the modulus of arg(z) is less than pi/4
Theorem: The following formula holds: $\dfrac{1}{2} \left( 1 + \mathrm{erf} \left( \dfrac{x-\mu}{\sqrt{2}\sigma} \right) \right)=\dfrac{1}{\sigma \sqrt{2 \pi}} \displaystyle\int_{-\infty}^x \exp \left( -\dfrac{(t-\mu)^2}{2\sigma^2} \right)\mathrm{d}t.$
Proof: █
Videos
The Laplace transform of the error function $\mathrm{erf}(t)$ (15 September 2013)
The Error function (8 November 2013)
Video 1690 - ERF Function (7 July 2015)
References
- 1956: Ian N. Sneddon: Special Functions of Mathematical Physics and Chemistry ... (previous) ... (next): $\S 5 (5.11)$
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): 7.1.1