Difference between revisions of "Polygamma"
(→Properties) |
|||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
=Properties= | =Properties= | ||
{{:Integral representation of polygamma}} | {{:Integral representation of polygamma}} | ||
| + | {{:Integral representation of polygamma 2}} | ||
=See Also= | =See Also= | ||
Revision as of 19:21, 3 June 2016
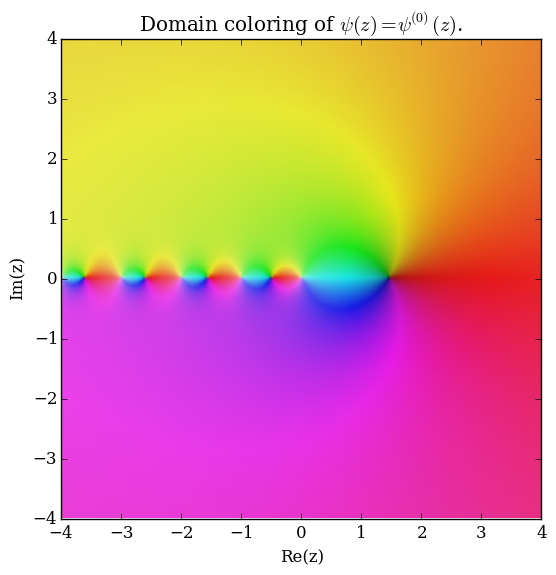
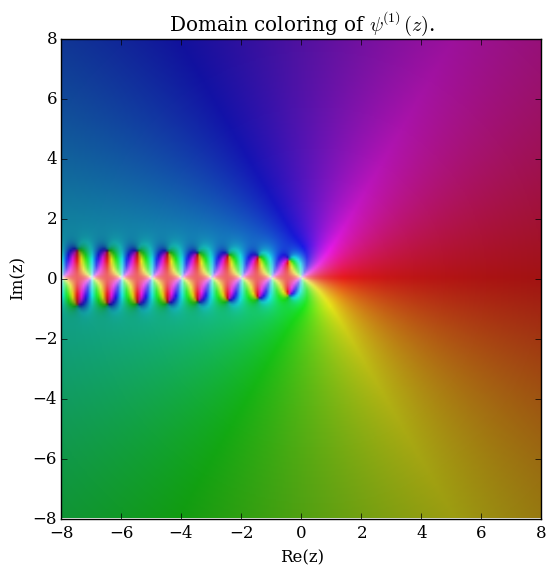
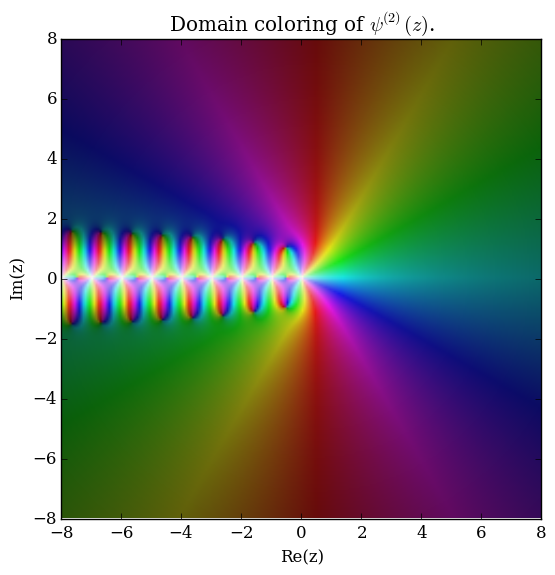
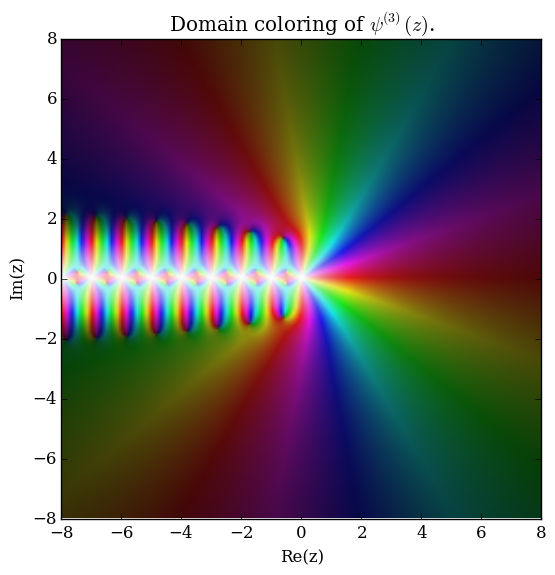
The polygamma function of order $m$, $\psi^{(m)}(z)$, is defined by the formula $$\psi^{(m)}(z) = \dfrac{\mathrm{d}^{m+1}}{\mathrm{d}z^{m+1}} \log \Gamma(z),$$ where $\log \Gamma$ denotes the loggamma function. The digamma function $\psi$ is the function $\psi^{(0)}(z)$ and the trigamma function is $\psi^{(1)}(z)$.
Contents
Properties
Theorem
The following formula holds for $\mathrm{Re}(z)>0$ and $m>0$: $$\psi^{(m)}(z)=(-1)^{m+1} \displaystyle\int_0^{\infty} \dfrac{t^m e^{-zt}}{1-e^{-t}} \mathrm{d}t,$$ where $\psi^{(m)}$ denotes the polygamma and $e^{-zt}$ denotes the exponential.
Proof
References
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): $6.4.1$
Theorem
The following formula holds for $\mathrm{Re}(z)>0$ and $m>0$: $$\psi^{(m)}(z)=-\displaystyle\int_0^1 \dfrac{t^{z-1}}{1-t} \log^m(t) \mathrm{d}t,$$ where $\psi^{(m)}$ denotes the polygamma and $\log$ denotes the logarithm.