Difference between revisions of "Sinc"
From specialfunctionswiki
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
=Properties= | =Properties= | ||
| − | + | [[Sum of values of sinc]]<br /> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | </ | ||
=Videos= | =Videos= | ||
Revision as of 08:02, 8 June 2016
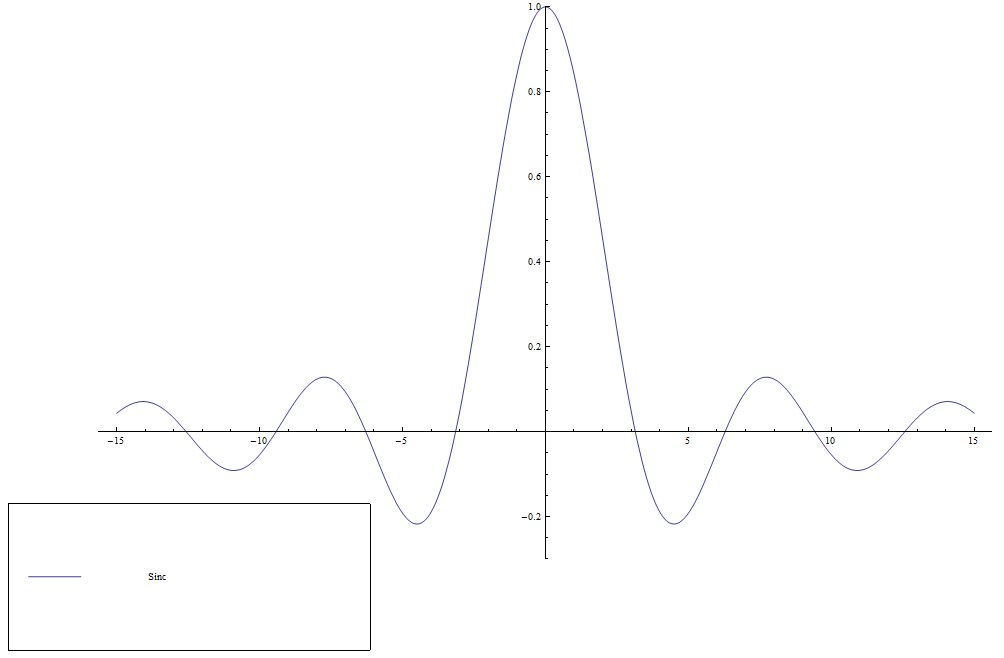
The $\mathrm{sinc}$ function (sometimes called the "unnormalized" $\mathrm{sinc}$ function) is defined by $$\mathrm{sinc}(z) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \dfrac{\sin z}{z} &; z \neq 0 \\ 1 &; z=0. \end{array} \right.$$ It appears in the definition of the Sine integral function.
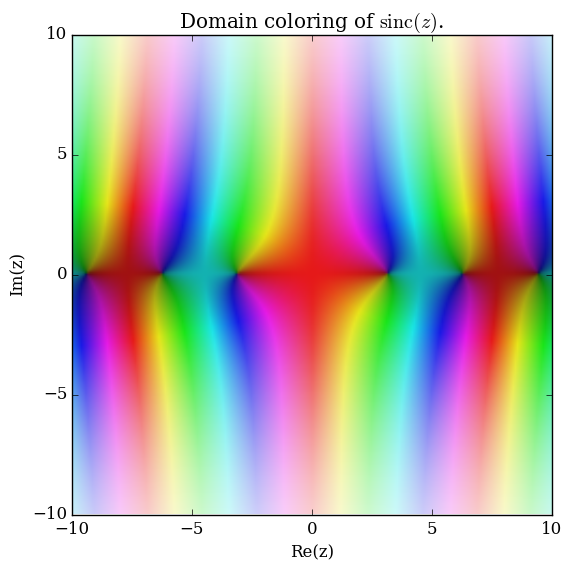
Domain coloring of $\mathrm{sinc}$.
Properties
Videos
Infinite Product Evaluation with the Sinc Function
(The Sinc Function) Inverse Fourier Transform of Sinc & Fourier Transform of Sinc
Fourier Transform of a Sinc Function (or Inverse Fourier Transform of a Low Pass Filter)
Discrete-Time Signals and Systems Introduction (4/6): Special Functions
Integrating the sinc function