Difference between revisions of "Sine integral"
From specialfunctionswiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The sine integral is defined by | The sine integral is defined by | ||
| − | $$\mathrm{Si}(z) = \displaystyle\int_0^z \mathrm{sinc}(t) \mathrm{d}t | + | $$\mathrm{Si}(z) = \displaystyle\int_0^z \mathrm{sinc}(t) \mathrm{d}t, \quad |\mathrm{arg} z|<\pi,$$ |
where $\mathrm{sinc}$ denotes the [[Sinc]] function. | where $\mathrm{sinc}$ denotes the [[Sinc]] function. | ||
Revision as of 05:41, 17 May 2016
The sine integral is defined by $$\mathrm{Si}(z) = \displaystyle\int_0^z \mathrm{sinc}(t) \mathrm{d}t, \quad |\mathrm{arg} z|<\pi,$$ where $\mathrm{sinc}$ denotes the Sinc function.
- Si.png
Graph of $\mathrm{Si}$.
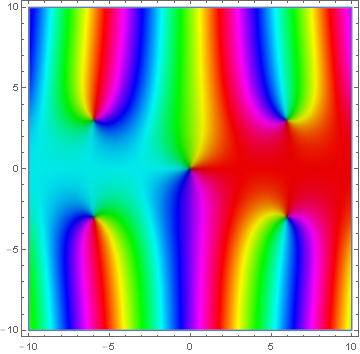
Domain coloring of analytic continuation of $\mathrm{Si}$.
Contents
Relationship to other functions
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\mathrm{Ei}(ix)=\mathrm{Ci}(x)+i\mathrm{Si}(x),$$ where $\mathrm{Ei}$ denotes the exponential integral Ei, $\mathrm{Ci}$ denotes the cosine integral, and $\mathrm{Si}$ denotes the sine integral.
Proof
References
Videos
Laplace Transform of Sine Integral