Difference between revisions of "Thomae function"
From specialfunctionswiki
(→Properties) |
|||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
<div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:800px"> | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:800px"> | ||
<strong>Theorem:</strong> The [[Thomae function]] $f(x)$ is [[Riemann integral|Riemann integrable]] and | <strong>Theorem:</strong> The [[Thomae function]] $f(x)$ is [[Riemann integral|Riemann integrable]] and | ||
| − | $$\displaystyle\int_0^1 f(x) | + | $$\displaystyle\int_0^1 f(x) \mathrm{d}x = 0.$$ |
<div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
<strong>Proof:</strong> █ | <strong>Proof:</strong> █ | ||
Revision as of 06:10, 25 May 2016
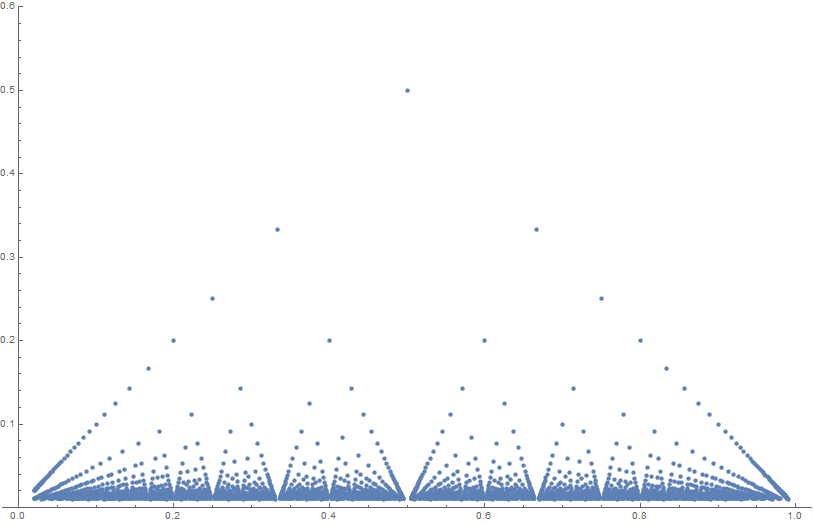
Thomae's function (sometimes called the popcorn function, raindrop function, Stars over Babylon) is given by the formula $$f(x) =\begin{cases} 1 & \text{if } x= 0 \\ \tfrac1{q} & \text{if } x = \tfrac{p}{q}\\ 0 & \text{if } x \in \mathbb{R}-\mathbb{Q}. \end{cases}$$
Contents
Properties
Theorem: The Thomae function is continuous at all irrational numbers and discontinuous at all rational numbers.
Proof: █
Theorem: The Thomae function has a (strict) local maximum at each rational number.
Proof: █
Theorem: The Thomae function $f(x)$ is Riemann integrable and $$\displaystyle\int_0^1 f(x) \mathrm{d}x = 0.$$
Proof: █
Videos
Thomae Function by Douglas Harder
Thomae Function by Bret Benesh
See also
Modifications of Thomae's Function and Differentiability