Difference between revisions of "Arctan"
(→Properties) |
|||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{:Relationship between arctan and hypergeometric 2F1}} | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
Revision as of 18:26, 20 May 2015
The $\mathrm{arctan}$ function is the inverse function of the tangent function.
- Arctan.png
Graph of $\mathrm{arctan}$ on $[-1,1]$.
- Complex arctan.jpg
Domain coloring of the analytic continuation of $\mathrm{arctan}$.
Properties
Proposition: $\dfrac{d}{dz} \mathrm{arctan}(z) = \dfrac{1}{z^2+1}$
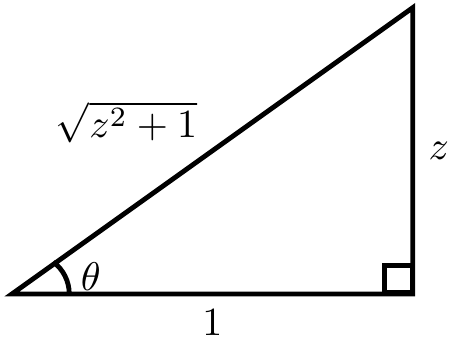
Proof: If $\theta=\mathrm{arctan}(z)$ then $\tan \theta = z$. Now use implicit differentiation with respect to $z$ yields $$\sec^2(\theta)\theta'=1.$$ The following triangle shows that $\sec^2(\mathrm{arctan}(z))=z^2+1$:
Substituting back in $\theta=\mathrm{arccos(z)}$ yields the formula $$\dfrac{d}{dz} \mathrm{arccos(z)} = \dfrac{1}{\sec^2(\mathrm{arctan(z)})} = \dfrac{1}{z^2+1}. █$$
Proposition: $\displaystyle\int \mathrm{arctan}(z) = z\mathrm{arctan}(z) - \dfrac{1}{2}\log(1+z^2)+C$
Proof: █
Proposition: $\mathrm{arctan}(z) = \mathrm{arccot}\left( \dfrac{1}{z} \right)$
Proof: █
Relationship between arctan and hypergeometric 2F1