Difference between revisions of "Logarithmic integral"
From specialfunctionswiki
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
<center>{{:*-integral functions footer}}</center> | <center>{{:*-integral functions footer}}</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:SpecialFunction]] | ||
Revision as of 18:47, 24 May 2016
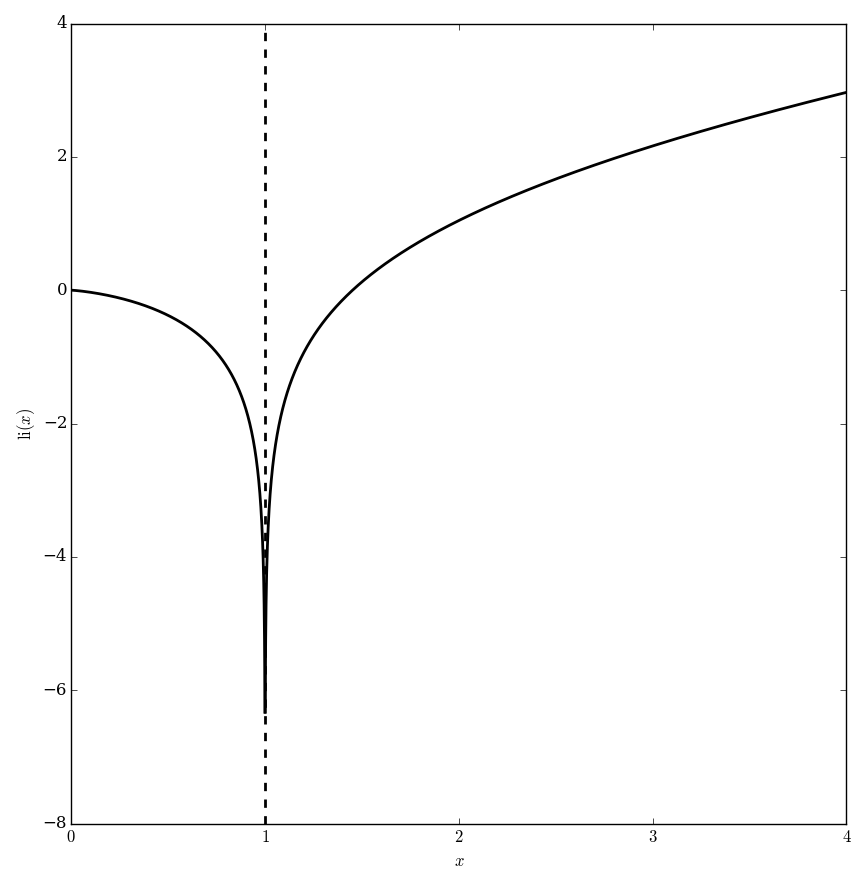
The logarithmic integral is $$\mathrm{li}(x) = \displaystyle\int_0^x \dfrac{1}{\log(t)} \mathrm{d}t,$$ where $\log$ denotes the logarithm.
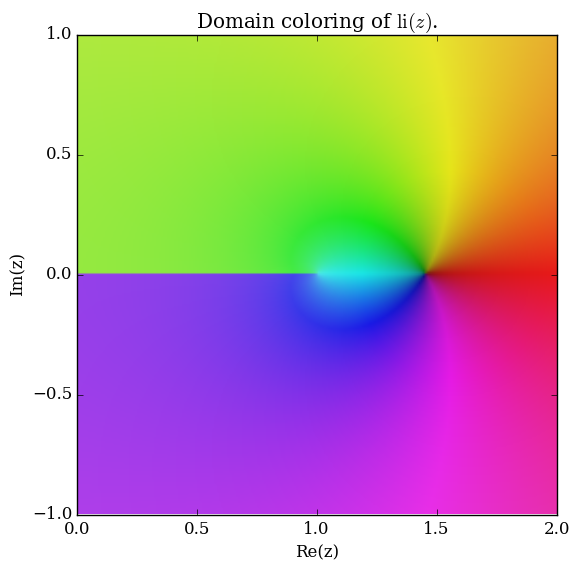
Domain coloring of $\mathrm{li}$.
Contents
Properties
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\mathrm{li}(x)=\mathrm{Ei}( \log(x)),$$ where $\mathrm{li}$ denotes the logarithmic integral, $\mathrm{Ei}$ denotes the exponential integral Ei, and $\log$ denotes the logarithm.
Proof
References
- James Whitbread Lee Glaisher: On certain definite integrals involving the exponential-integral (1881)... (previous)... (next) (note: expresses this relationship as $\mathrm{Ei}(x)=\mathrm{li}(e^x)$)
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\lim_{x \rightarrow \infty} \dfrac{\pi(x)}{\mathrm{li}(x)}=1,$$ where $\pi$ denotes the prime counting function and $\mathrm{li}$ denotes the logarithmic integral.