Difference between revisions of "Gamma"
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | * {{BookReference|A course of modern analysis|1920|Edmund Taylor Whittaker|author2=George Neville Watson|prev=findme|next=Euler-Mascheroni constant}}: | + | * {{BookReference|A course of modern analysis|1920|Edmund Taylor Whittaker|author2=George Neville Watson|prev=findme|next=Euler-Mascheroni constant}}: $\S 12 \cdot 1$ |
* {{BookReference|Higher Transcendental Functions Volume I|1953|Harry Bateman|next=Gamma(z) as integral of a power of log(1/t) for Re(z) greater than 0}}: §1.1 (1) | * {{BookReference|Higher Transcendental Functions Volume I|1953|Harry Bateman|next=Gamma(z) as integral of a power of log(1/t) for Re(z) greater than 0}}: §1.1 (1) | ||
* {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev=findme|next=Gauss' formula for gamma function}}: 6.1.1 | * {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev=findme|next=Gauss' formula for gamma function}}: 6.1.1 | ||
Revision as of 01:41, 12 June 2016
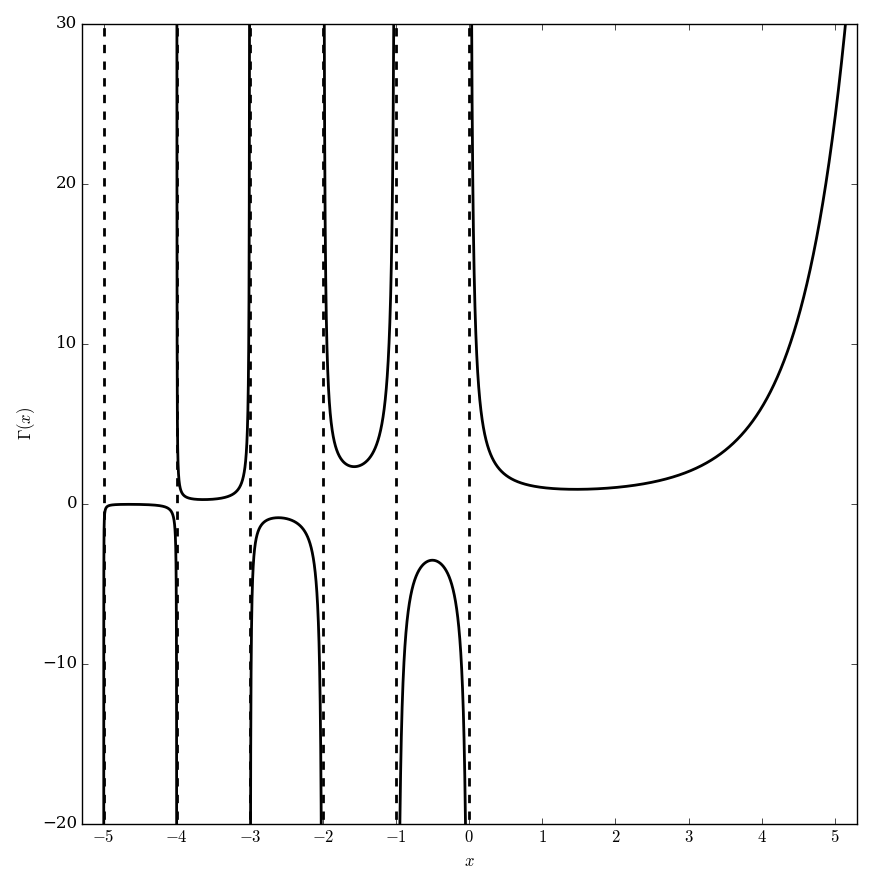
The gamma function $\Gamma \colon \mathbb{C} \setminus \{0,-1,-2,\ldots\} \rightarrow \mathbb{C}$ is the function initially defined for $\mathrm{Re}(z)>0$ by the integral by the formula $$\Gamma(x)=\displaystyle\int_0^{\infty} \xi^{x-1}e^{-\xi} \mathrm{d}\xi.$$ The analytic continuation of $\Gamma$ leads to a meromorphic function with poles at the negative integers.
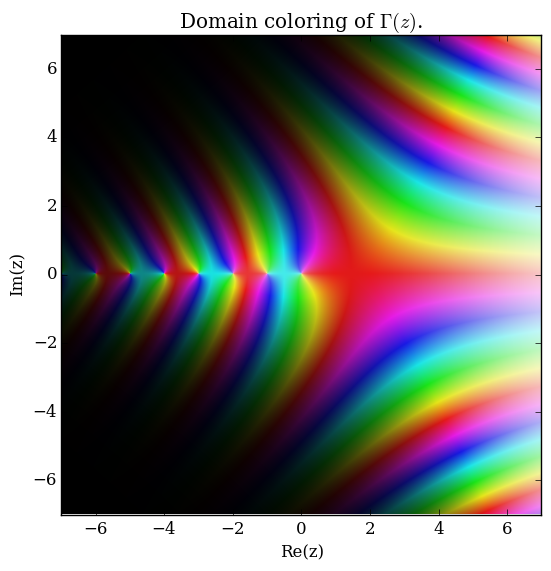
Domain coloring of $\Gamma$.
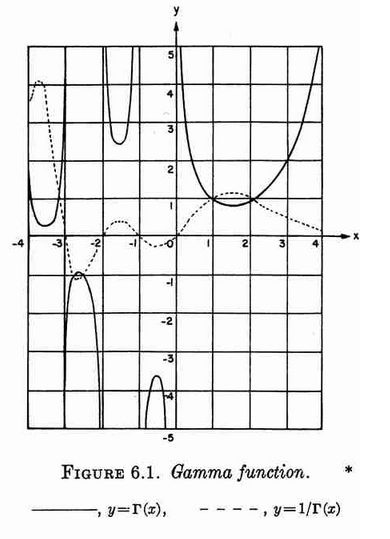
Plot of $\Gamma$ and $\dfrac{1}{\Gamma}$ from Abramowitz&Stegun.
Contents
Properties
Gamma(z) as integral of a power of log(1/t) for Re(z) greater than 0
Gamma function written as a limit of a factorial, exponential, and a rising factorial
Gamma function written as infinite product
Value of Gamma(1)
Factorial property of gamma
Gamma at positive integers
Gamma function Weierstrass product
Relationship between Hurwitz zeta and gamma function
Gamma-Sine Relation
Bohr-Mollerup theorem
Videos
Gamma Function (playlist)
The Gamma Function: intro (5)
Gamma Integral Function - Introduction
Gamma function
Mod-04 Lec-09 Analytic continuation and the gamma function (Part I)
gamma function - Part 1
Beta Function, Gamma Function and their Properties
What's the Gamma Function?
euler gamma function
Thermodynamics 19 a : Gamma Function 1/2
The Gamma Function: why 0!=1 (5)
Gamma Function Of One-Half: Part 1
Gamma Function Of One-Half: Part 2
Gamma function at 1/2
Contour Integral Definition of the Gamma Function
See Also
Loggamma
Polygamma
Reciprocal gamma
References
- 1920: Edmund Taylor Whittaker and George Neville Watson: A course of modern analysis ... (previous) ... (next): $\S 12 \cdot 1$
- 1953: Harry Bateman: Higher Transcendental Functions Volume I ... (next): §1.1 (1)
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): 6.1.1
The Gamma Function by Emil Artin
The sine product formula and the gamma function
Leonhard Euler's Integral: A Historical Profile of the Gamma Function