Difference between revisions of "Derivative of arcsec"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Proof== | ==Proof== | ||
| − | + | If $\theta=\mathrm{arcsec}(z)$ then $\sec(\theta)=z$. Now use [[implicit differentiation]] with respect to $z$ and the [[derivative of secant]] to see | |
| + | $$\sec(\theta)\tan(\theta) \theta' = 1,$$ | ||
| + | or equivalently, | ||
| + | $$\dfrac{\mathrm{d}\theta}{\mathrm{d}z} = \dfrac{1}{\sec(\theta)\tan(\theta)} = \dfrac{1}{z\tan(\theta)}.$$ | ||
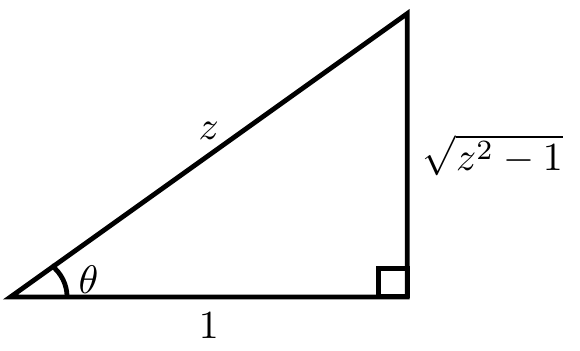
| + | The following image shows that $\tan(\mathrm{arcsec}(z))=\sqrt{z^2-1}$: | ||
| + | [[File:Tan(arcsec(z)).png|200px|center]] | ||
| + | Hence substituting back in $\theta=\mathrm{arcsec}(z)$ yields the formula | ||
| + | $$\dfrac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d}z} \mathrm{arcsec}(z) = \dfrac{1}{z\tan(\mathrm{arcsec}(z))} = \dfrac{1}{z\sqrt{z^2-1}}=\dfrac{1}{z^2\sqrt{1-\frac{1}{z^2}}},$$ | ||
| + | as was to be shown. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[[Category:Theorem]] | [[Category:Theorem]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Proven]] |
Latest revision as of 23:51, 8 December 2016
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\dfrac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d}z} \mathrm{arcsec}(z) = \dfrac{1}{z^2\sqrt{1-\frac{1}{z^2}}},$$ where $\mathrm{arcsec}$ is the inverse secant function.
Proof
If $\theta=\mathrm{arcsec}(z)$ then $\sec(\theta)=z$. Now use implicit differentiation with respect to $z$ and the derivative of secant to see $$\sec(\theta)\tan(\theta) \theta' = 1,$$ or equivalently, $$\dfrac{\mathrm{d}\theta}{\mathrm{d}z} = \dfrac{1}{\sec(\theta)\tan(\theta)} = \dfrac{1}{z\tan(\theta)}.$$ The following image shows that $\tan(\mathrm{arcsec}(z))=\sqrt{z^2-1}$:
Hence substituting back in $\theta=\mathrm{arcsec}(z)$ yields the formula $$\dfrac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d}z} \mathrm{arcsec}(z) = \dfrac{1}{z\tan(\mathrm{arcsec}(z))} = \dfrac{1}{z\sqrt{z^2-1}}=\dfrac{1}{z^2\sqrt{1-\frac{1}{z^2}}},$$ as was to be shown.