Difference between revisions of "Bessel Y"
From specialfunctionswiki
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | Bessel functions of the second kind $Y_{\nu}$ are defined via the formula | + | Bessel functions of the second kind, $Y_{\nu}$, are defined via the formula |
$$Y_{\nu}(z)=\dfrac{J_{\nu}(z)\cos(\nu \pi)-J_{-\nu}(z)}{\sin(\nu \pi)}.$$ | $$Y_{\nu}(z)=\dfrac{J_{\nu}(z)\cos(\nu \pi)-J_{-\nu}(z)}{\sin(\nu \pi)}.$$ | ||
Sometimes these functions are called Neumann functions and have the notation $N_{\nu}$ instead of $Y_{\nu}$. | Sometimes these functions are called Neumann functions and have the notation $N_{\nu}$ instead of $Y_{\nu}$. | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
<div align="center"> | <div align="center"> | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
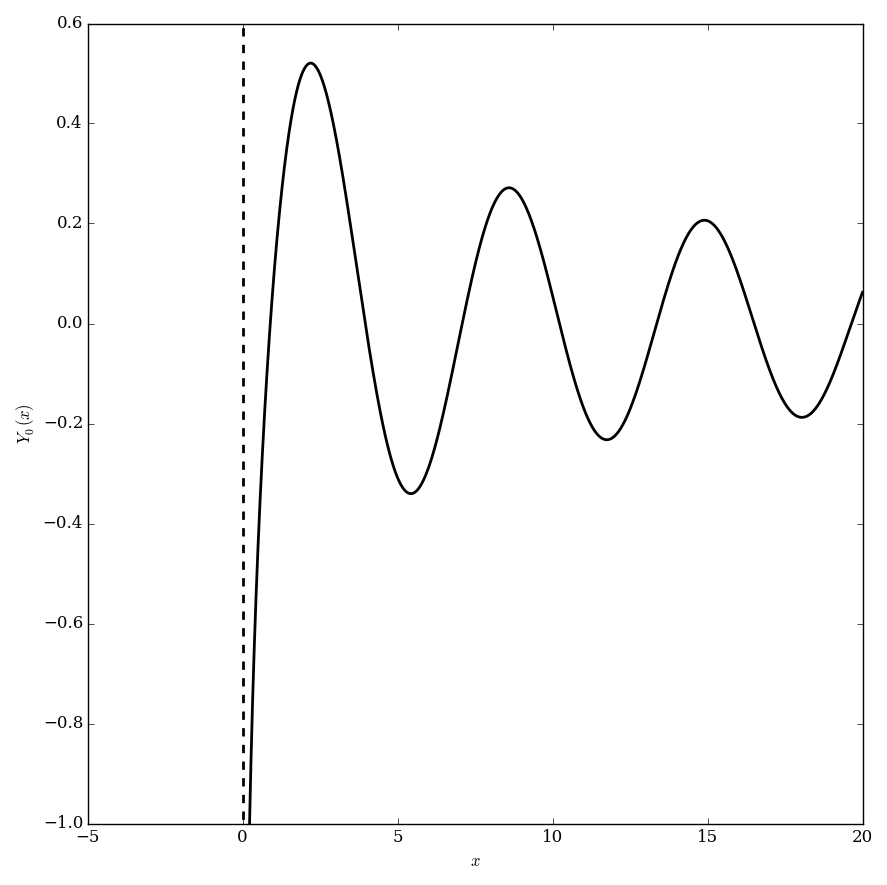
| − | File: | + | File:Bessely,n=0plot.png|Graph of $Y_0$. |
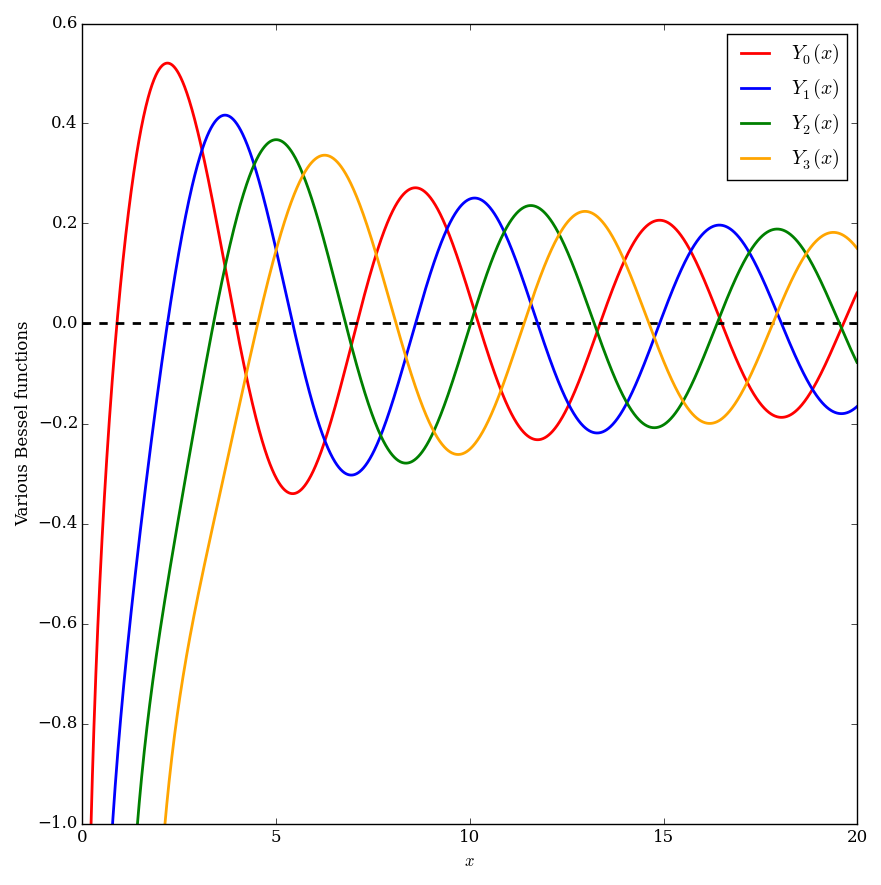
| − | File: | + | File:Multiplebesselyplot.png|Graph of $Y_0,Y_1,Y_2$, and $Y_3$. |
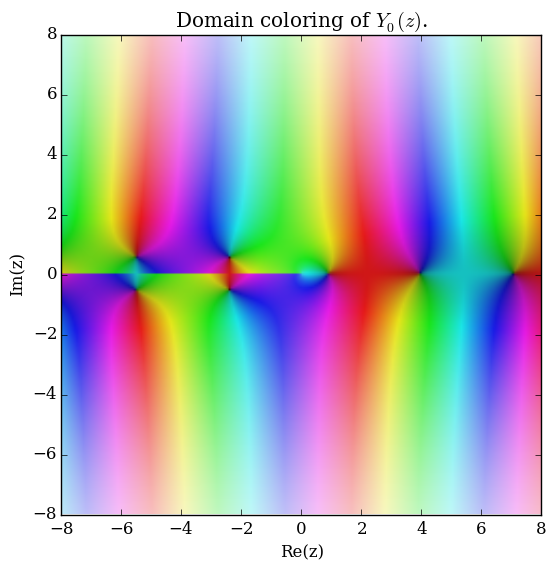
| − | File: | + | File:Complexbessely,n=0.png|[[Domain coloring]] of $Y_0$. |
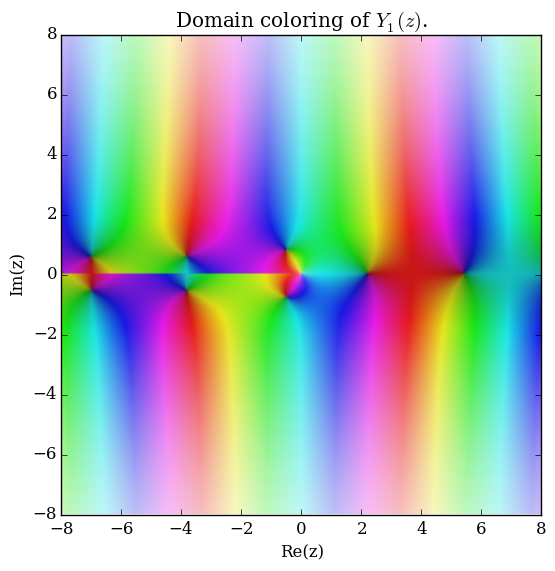
| + | File:Complexbessely,n=1.png|[[Domain coloring]] of $Y_1$. | ||
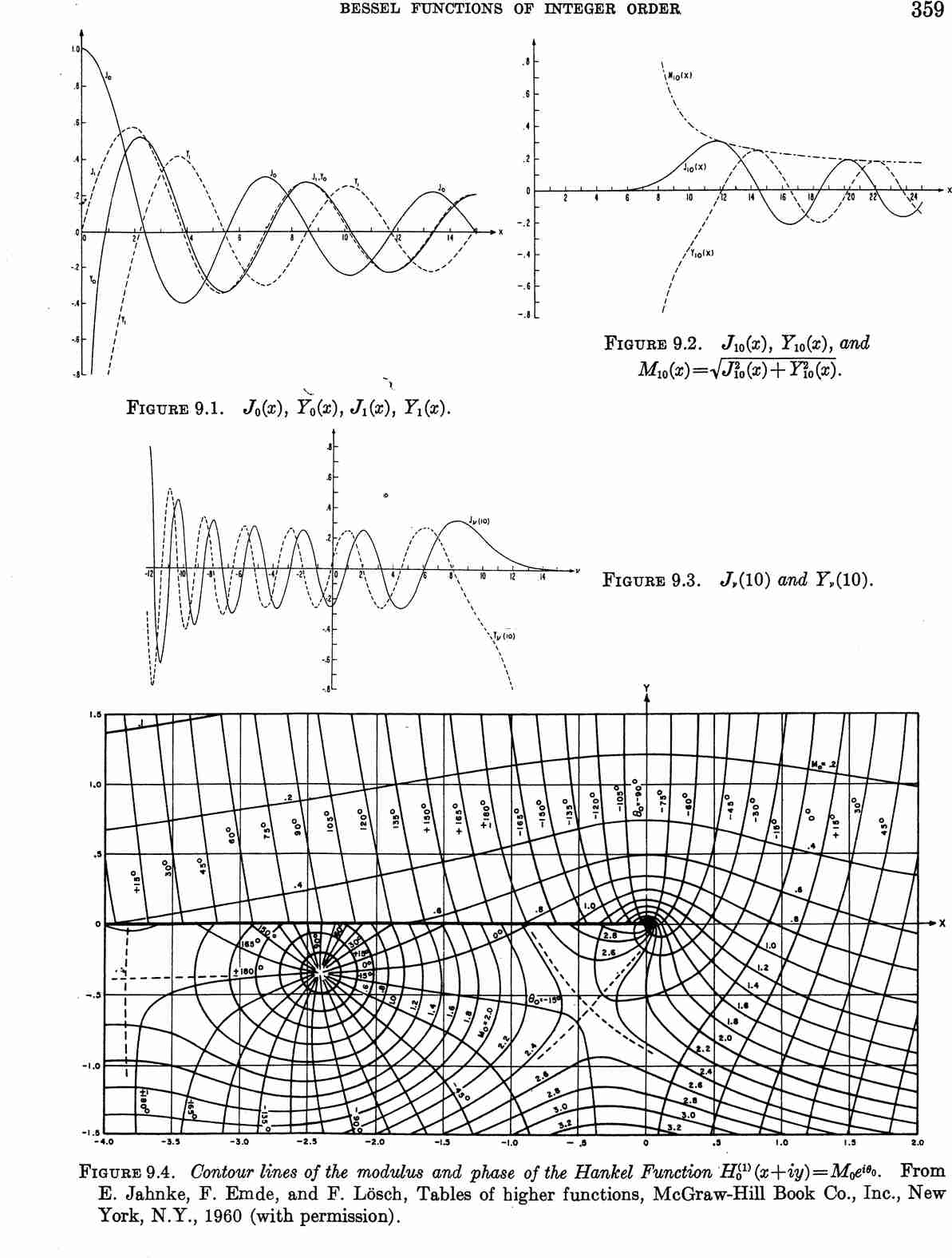
File:Page 359Abramowitz-Stegun(Bessel functions).jpg|Bessel functions from [http://dualaud.net/specialfunctionswiki/abramowitz_and_stegun-1.03/ Abramowitz&Stegun] | File:Page 359Abramowitz-Stegun(Bessel functions).jpg|Bessel functions from [http://dualaud.net/specialfunctionswiki/abramowitz_and_stegun-1.03/ Abramowitz&Stegun] | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
=Properties= | =Properties= | ||
| − | + | [[Derivative of Bessel Y with respect to its order]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=References= | =References= | ||
| + | * {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev=findme|next=Hankel H (1)}}: 9.1.2 | ||
[http://gdz.sub.uni-goettingen.de/dms/load/img/?PID=PPN600494829_0021%7CLOG_0023 Bessel's functions of the second order - C.V. Coates]<br /> | [http://gdz.sub.uni-goettingen.de/dms/load/img/?PID=PPN600494829_0021%7CLOG_0023 Bessel's functions of the second order - C.V. Coates]<br /> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | {{:Bessel functions footer}} | ||
[[Category:SpecialFunction]] | [[Category:SpecialFunction]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:39, 10 July 2017
Bessel functions of the second kind, $Y_{\nu}$, are defined via the formula $$Y_{\nu}(z)=\dfrac{J_{\nu}(z)\cos(\nu \pi)-J_{-\nu}(z)}{\sin(\nu \pi)}.$$ Sometimes these functions are called Neumann functions and have the notation $N_{\nu}$ instead of $Y_{\nu}$.
Domain coloring of $Y_0$.
Domain coloring of $Y_1$.
Bessel functions from Abramowitz&Stegun
Properties
Derivative of Bessel Y with respect to its order
References
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): 9.1.2
Bessel's functions of the second order - C.V. Coates