Difference between revisions of "Digamma"
From specialfunctionswiki
(→See Also) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
=See Also= | =See Also= | ||
| − | [[Gamma | + | [[Gamma]] <br /> |
[[Polygamma]]<br /> | [[Polygamma]]<br /> | ||
[[Trigamma]] <br /> | [[Trigamma]] <br /> | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | * {{BookReference|Higher Transcendental Functions Volume I|1953| | + | * {{BookReference|Higher Transcendental Functions Volume I|1953|Arthur Erdélyi|author2=Wilhelm Magnus|author3=Fritz Oberhettinger|author4=Francesco G. Tricomi|prev=findme|next=findme}}: $\S 1.7 (1)$ |
* {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev=Beta is symmetric|next=Digamma at 1}}: $6.3.1$ | * {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev=Beta is symmetric|next=Digamma at 1}}: $6.3.1$ | ||
[[Category:SpecialFunction]] | [[Category:SpecialFunction]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:21, 3 March 2018
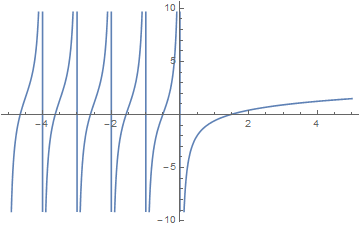
The digamma function $\psi \colon \mathbb{C} \setminus \{0,-1,-2,\ldots\} \rightarrow \mathbb{C}$ is defined by $$\psi(z) = \dfrac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d}z} \log \Gamma(z) = \dfrac{\Gamma'(z)}{\Gamma(z)}.$$
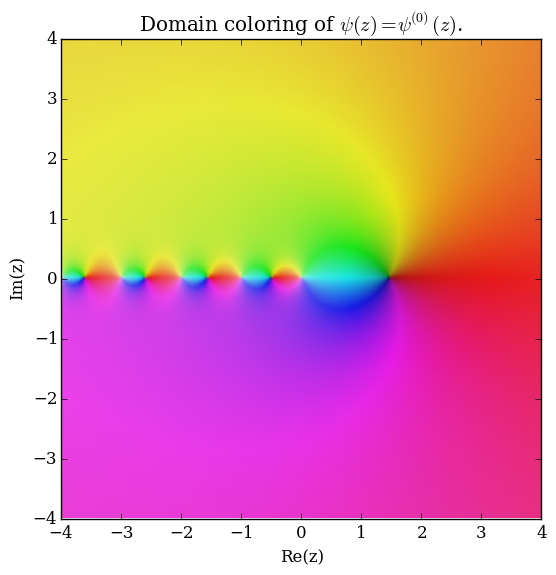
Domain coloring of $\psi(z)$.
Properties
Partial derivative of beta function
Digamma at 1
Digamma functional equation
Digamma at n+1
See Also
References
- 1953: Arthur Erdélyi, Wilhelm Magnus, Fritz Oberhettinger and Francesco G. Tricomi: Higher Transcendental Functions Volume I ... (previous) ... (next): $\S 1.7 (1)$
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): $6.3.1$