Difference between revisions of "Exponential integral E"
From specialfunctionswiki
(→References) |
|||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | * {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev=findme|next=Exponential integral Ei}}: $5.1.1$ | + | * {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev=findme|next=Exponential integral Ei}}: $5.1.1$ (<i>note: this formula only defines it for $n=1$</i>) |
| − | * {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev=findme|next=findme}}: $5.1.4$ | + | * {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev=findme|next=findme}}: $5.1.4$ (<i>note:</i> this formula defines it for $n=0,1,2,\ldots$) |
{{:*-integral functions footer}} | {{:*-integral functions footer}} | ||
[[Category:SpecialFunction]] | [[Category:SpecialFunction]] | ||
Revision as of 00:05, 24 March 2018
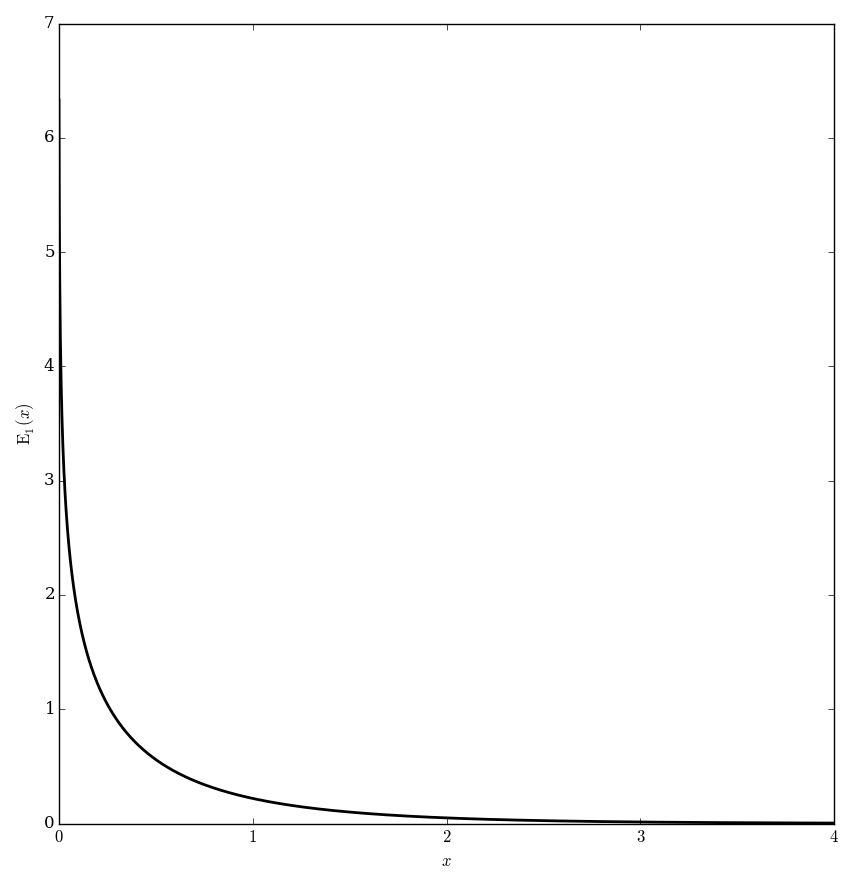
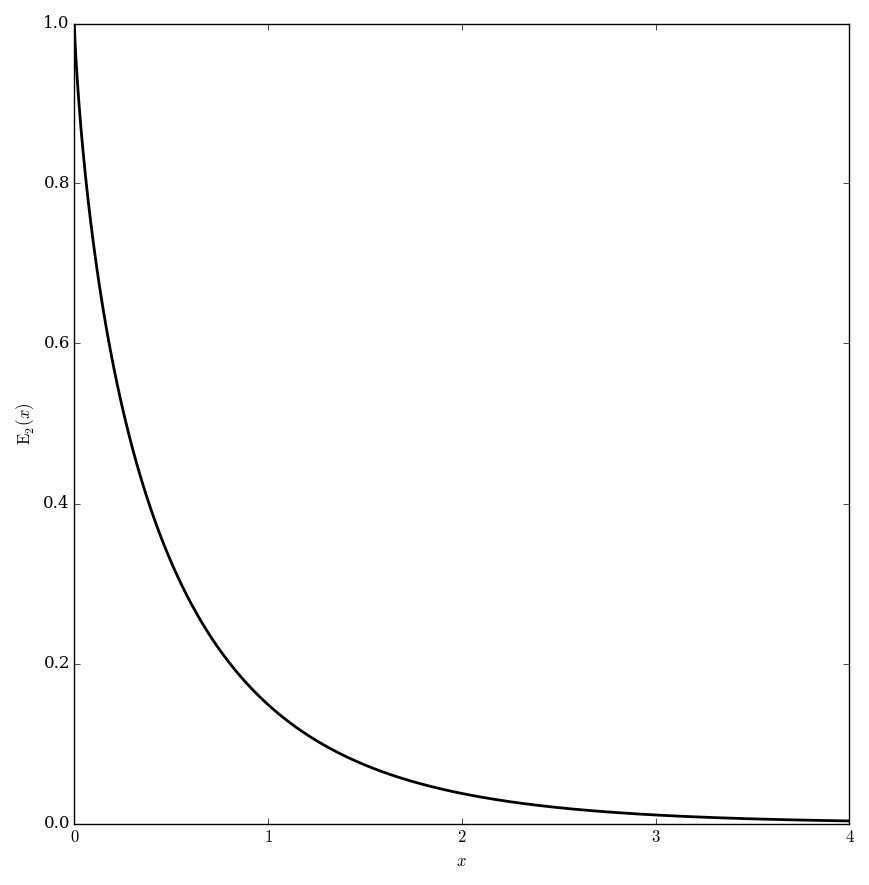
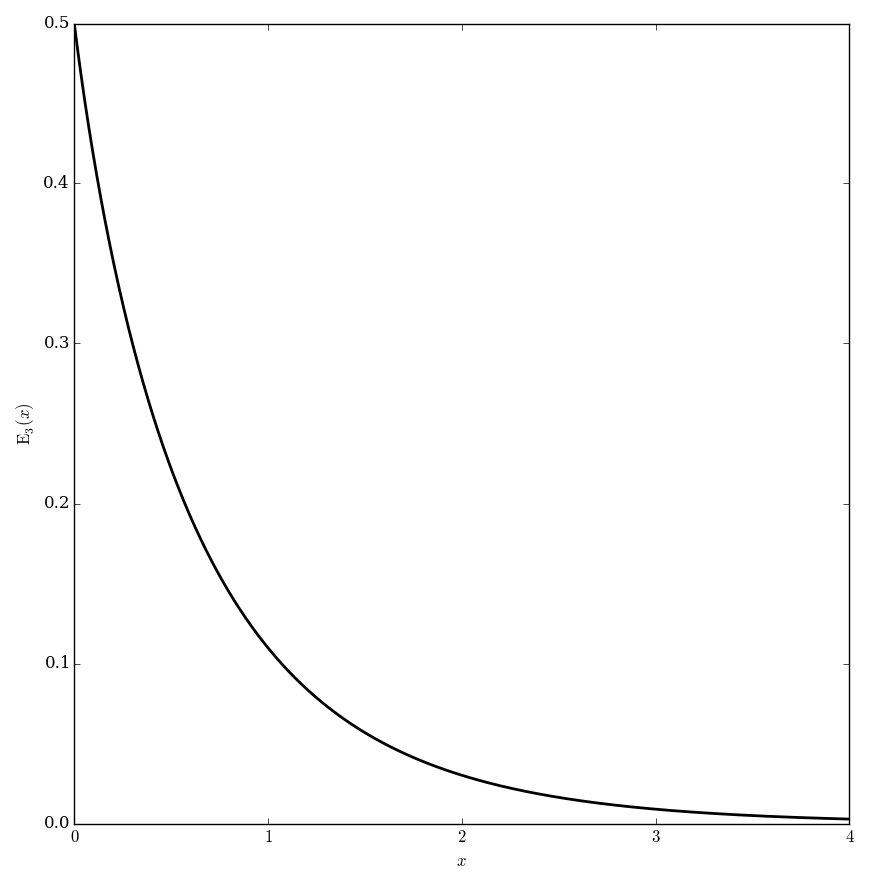
The exponential integral functions $E_n$ are defined for $\left|\mathrm{arg \hspace{2pt}}z\right|<\pi$ and $n=1,2,3,\ldots$ by $$E_n(z)=\displaystyle\int_1^{\infty} \dfrac{e^{-zt}}{t^n} \mathrm{d}t.$$
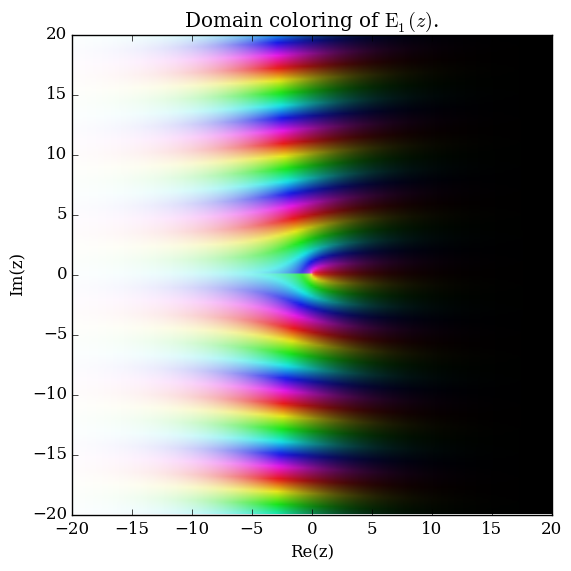
Domain coloring of $\mathrm{E}_1$.
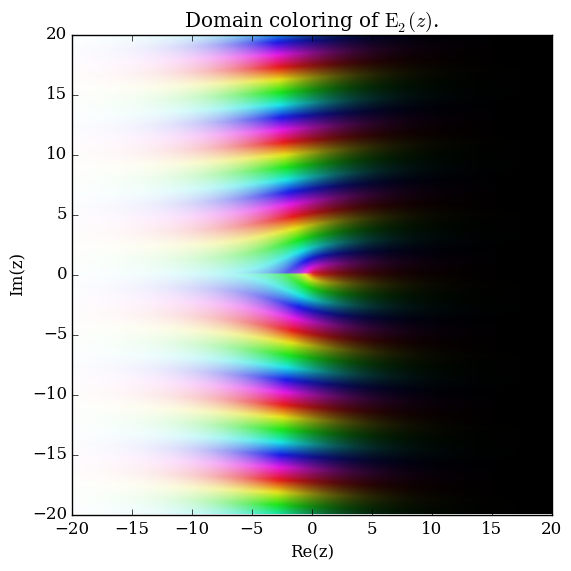
Domain coloring of $\mathrm{E}_2$.
Properties
Relationship between the exponential integral and upper incomplete gamma function
Symmetry relation of exponential integral E
Recurrence relation of exponential integral E
Videos
Laplace transform of exponential integral (2 January 2015)
See Also
References
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): $5.1.1$ (note: this formula only defines it for $n=1$)
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): $5.1.4$ (note: this formula defines it for $n=0,1,2,\ldots$)