Difference between revisions of "Exponential integral Ei"
From specialfunctionswiki
(→References) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
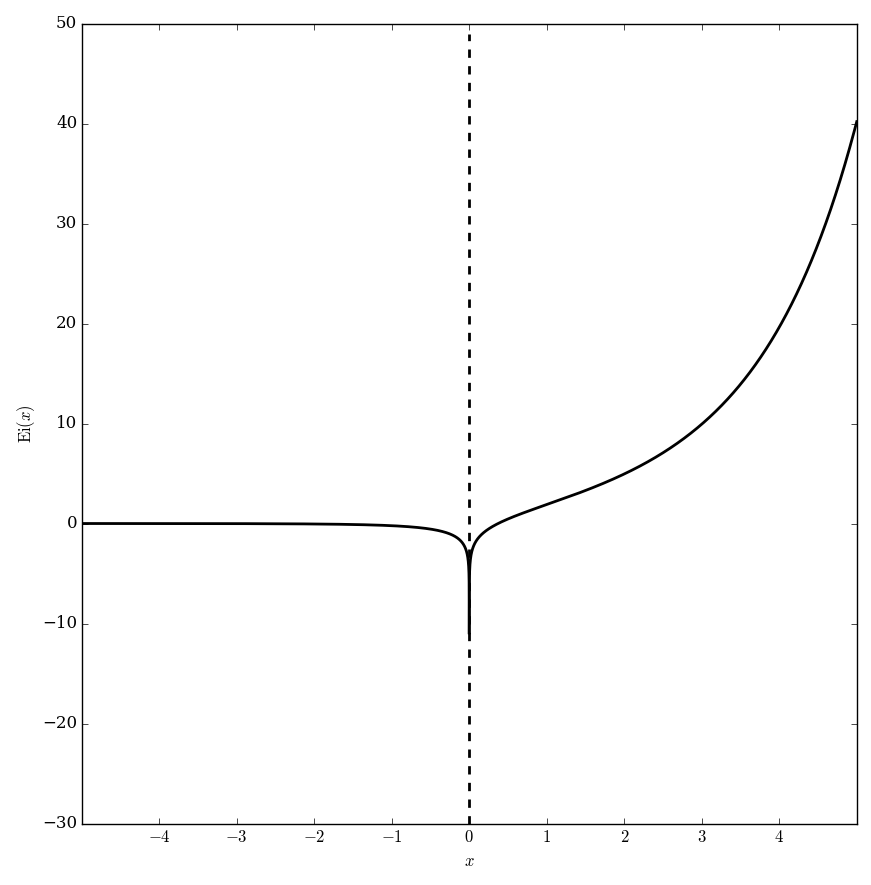
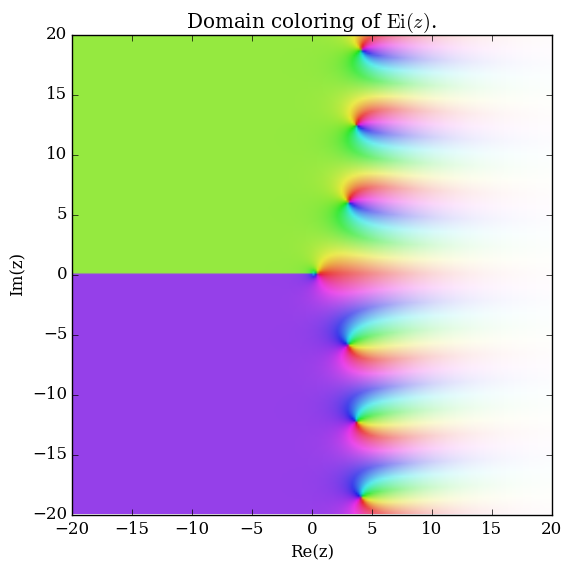
The exponential integral $\mathrm{Ei}$ is defined for $x>0$ by | The exponential integral $\mathrm{Ei}$ is defined for $x>0$ by | ||
$$\mathrm{Ei}(x) = \mathrm{PV}\int_{-\infty}^x \dfrac{e^t}{t} \mathrm{d}t,$$ | $$\mathrm{Ei}(x) = \mathrm{PV}\int_{-\infty}^x \dfrac{e^t}{t} \mathrm{d}t,$$ | ||
| − | where $\mathrm{PV}$ denotes the [[Cauchy principal value]]. | + | where $\mathrm{PV}$ denotes the [[Cauchy principal value]] and $e^t$ denotes the [[exponential]]. |
Latest revision as of 00:48, 24 March 2018
The exponential integral $\mathrm{Ei}$ is defined for $x>0$ by $$\mathrm{Ei}(x) = \mathrm{PV}\int_{-\infty}^x \dfrac{e^t}{t} \mathrm{d}t,$$ where $\mathrm{PV}$ denotes the Cauchy principal value and $e^t$ denotes the exponential.
Properties
Ei(-x)=-Integral from -x to infinity of e^(-t)/t dt
Relationship between logarithmic integral and exponential integral
Exponential integral Ei series
Relationship between exponential integral Ei, cosine integral, and sine integral
See Also
References
- James Whitbread Lee Glaisher: On certain definite integrals involving the exponential-integral (1881)... (next)
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): $5.1.2$