Difference between revisions of "Hankel H (2)"
From specialfunctionswiki
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The Hankel functions of the second kind are defined by | The Hankel functions of the second kind are defined by | ||
$$H_{\nu}^{(2)}(z)=J_{\nu}(z)-iY_{\nu}(z),$$ | $$H_{\nu}^{(2)}(z)=J_{\nu}(z)-iY_{\nu}(z),$$ | ||
| − | where $J_{\nu}$ is the [[Bessel J | + | where $J_{\nu}$ is the [[Bessel J|Bessel function of the first kind]] and $Y_{\nu}$ is the [[Bessel Y|Bessel function of the second kind]]. Note the similarity of these functions to the [[Hankel H (1)|Hankel functions of the first kind]]. |
<div align="center"> | <div align="center"> | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
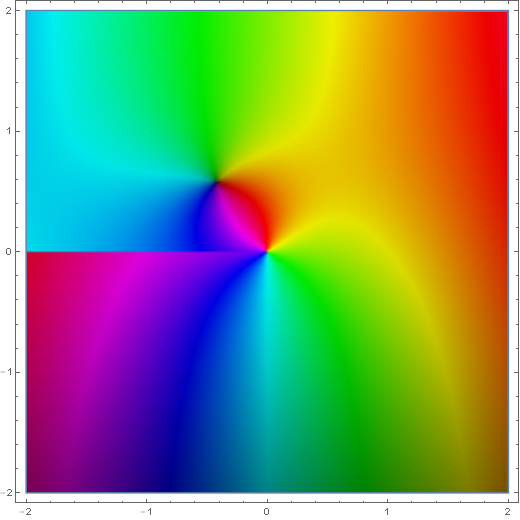
| − | File:Complex hankel H2 sub 1.png|[[Domain coloring | + | File:Complex hankel H2 sub 1.png|[[Domain coloring]] of $H_1^{(2)}(z)$. |
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | < | + | =See Also= |
| + | [[Bessel J|Bessel $J$]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Bessel Y|Bessel $Y$]]<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =References= | ||
| + | * {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev=Hankel H (1) in terms of csc and Bessel J|next=Hankel H (2) in terms of csc and Bessel J}}: 9.1.4 | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{:Hankel functions footer}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:SpecialFunction]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:58, 22 December 2016
The Hankel functions of the second kind are defined by $$H_{\nu}^{(2)}(z)=J_{\nu}(z)-iY_{\nu}(z),$$ where $J_{\nu}$ is the Bessel function of the first kind and $Y_{\nu}$ is the Bessel function of the second kind. Note the similarity of these functions to the Hankel functions of the first kind.
Domain coloring of $H_1^{(2)}(z)$.
See Also
References
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): 9.1.4
Hankel $H_{\nu}^{(2)}$