Difference between revisions of "Mangoldt"
From specialfunctionswiki
(→Videos) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | __NOTOC__ | ||
The Mangoldt function is defined by the formula | The Mangoldt function is defined by the formula | ||
$$\Lambda(n) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} | $$\Lambda(n) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} | ||
| − | \log p & | + | \log p, & n=p^k \mathrm{\hspace{2pt}for\hspace{2pt}some\hspace{2pt}prime\hspace{2pt}}p\mathrm{\hspace{2pt}and\hspace{2pt}integer\hspace{2pt}}k\geq 1, \\ |
| − | 0 & | + | 0, & \mathrm{otherwise}. |
\end{array} \right.$$ | \end{array} \right.$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div align="center"> | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
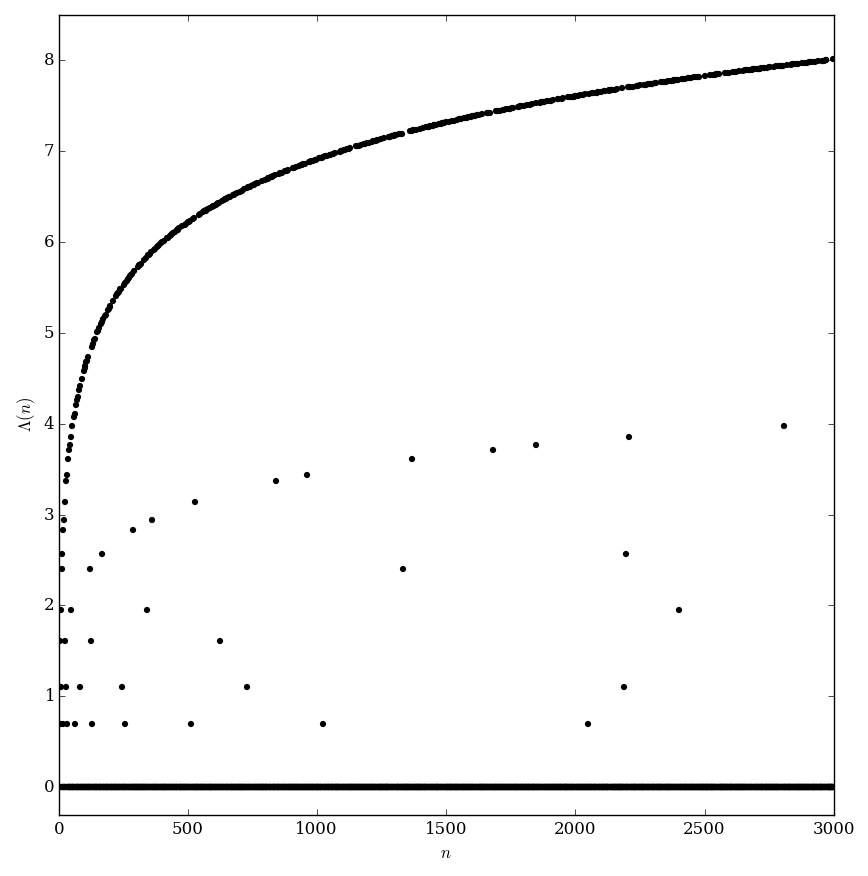
| + | File:Mangoldtplot.png|Graph of $\Lambda$. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
=Properties= | =Properties= | ||
| − | + | [[Relationship between logarithm and Mangoldt]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=Videos= | =Videos= | ||
| − | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KTPGc4170uo Number Theory 31: Liouville and mangoldt functions]<br /> | + | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KTPGc4170uo Number Theory 31: Liouville and mangoldt functions] (8 January 2015)<br /> |
| − | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X0XJ3TuMiFc Number theory: Arithmetic functions #1]<br /> | + | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X0XJ3TuMiFc Number theory: Arithmetic functions #1] (27 July 2012)<br /> |
| + | |||
| + | =References= | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{:Number theory functions footer}} | ||
[[Category:SpecialFunction]] | [[Category:SpecialFunction]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:31, 28 November 2016
The Mangoldt function is defined by the formula $$\Lambda(n) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \log p, & n=p^k \mathrm{\hspace{2pt}for\hspace{2pt}some\hspace{2pt}prime\hspace{2pt}}p\mathrm{\hspace{2pt}and\hspace{2pt}integer\hspace{2pt}}k\geq 1, \\ 0, & \mathrm{otherwise}. \end{array} \right.$$
Properties
Relationship between logarithm and Mangoldt
Videos
Number Theory 31: Liouville and mangoldt functions (8 January 2015)
Number theory: Arithmetic functions #1 (27 July 2012)