Difference between revisions of "Sinc"
From specialfunctionswiki
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
[https://youtu.be/3Sjn3XLo5XE?t=306 Discrete-Time Signals and Systems Introduction (4/6): Special Functions]<br /> | [https://youtu.be/3Sjn3XLo5XE?t=306 Discrete-Time Signals and Systems Introduction (4/6): Special Functions]<br /> | ||
[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xx2AQz_ZyC0 Integrating the sinc function]<br /> | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xx2AQz_ZyC0 Integrating the sinc function]<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =See also= | ||
| + | [[Normalized sinc]]<br /> | ||
{{:*-c functions footer}} | {{:*-c functions footer}} | ||
[[Category:SpecialFunction]] | [[Category:SpecialFunction]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:19, 16 September 2016
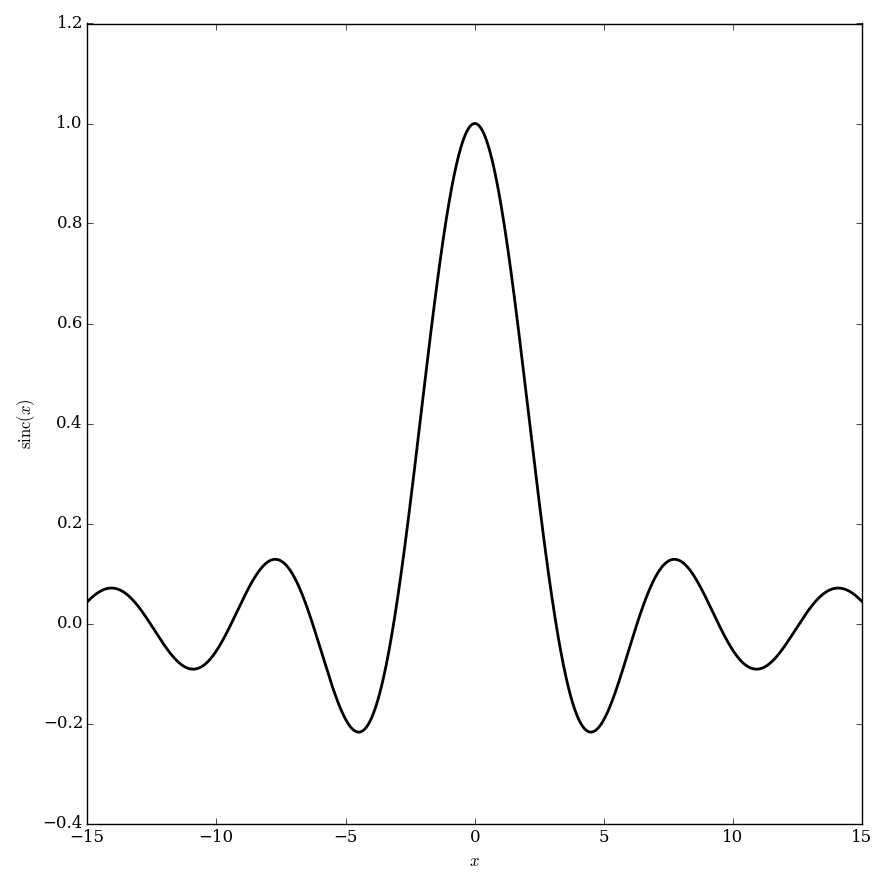
The $\mathrm{sinc}$ function (sometimes called the "unnormalized" $\mathrm{sinc}$ function) is defined by $$\mathrm{sinc}(z) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \dfrac{\sin z}{z} &; z \neq 0 \\ 1 &; z=0. \end{array} \right.$$ It appears in the definition of the Sine integral function.
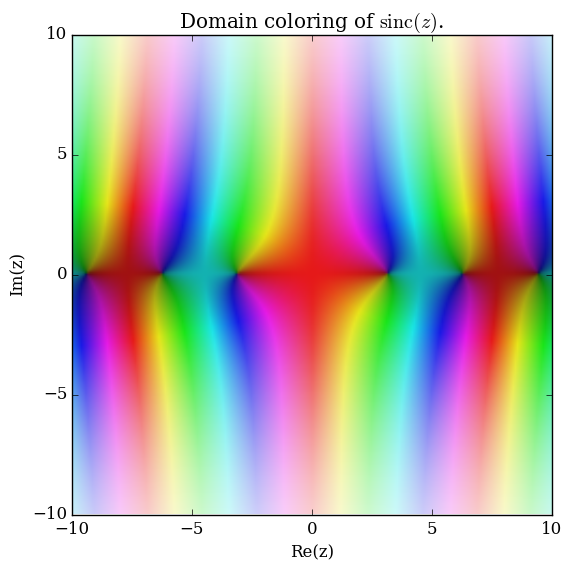
Domain coloring of $\mathrm{sinc}$.
Properties
Videos
Infinite Product Evaluation with the Sinc Function
(The Sinc Function) Inverse Fourier Transform of Sinc & Fourier Transform of Sinc
Fourier Transform of a Sinc Function (or Inverse Fourier Transform of a Low Pass Filter)
Discrete-Time Signals and Systems Introduction (4/6): Special Functions
Integrating the sinc function