Difference between revisions of "Arccos"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
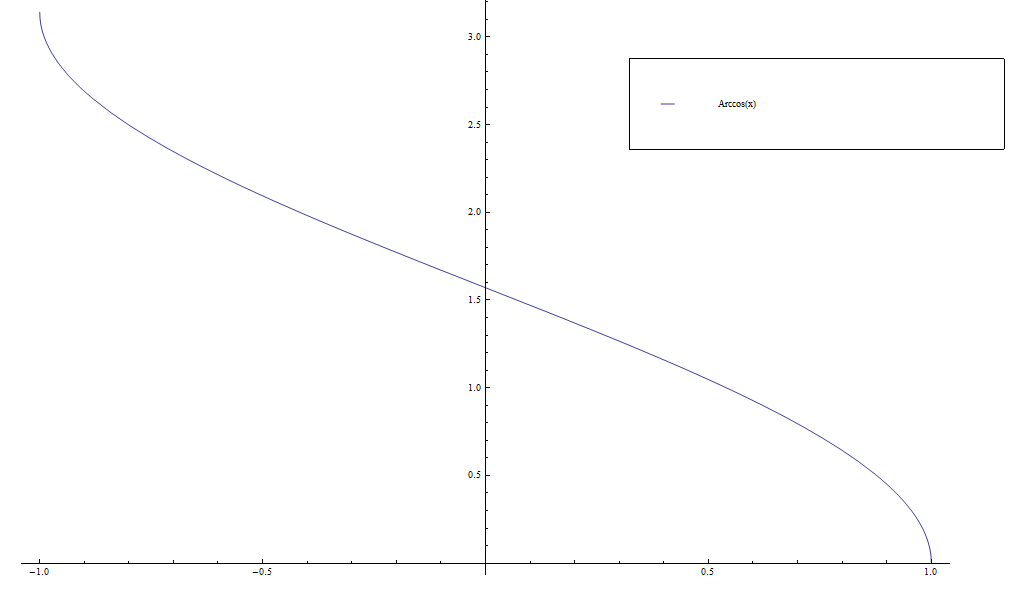
The function $\mathrm{arccos} \colon [-1,1] \longrightarrow [0,\pi]$ is the [[inverse function]] of the [[cosine]] function. | The function $\mathrm{arccos} \colon [-1,1] \longrightarrow [0,\pi]$ is the [[inverse function]] of the [[cosine]] function. | ||
| − | + | <gallery> | |
| + | File:Arccos.png|Graph of $\mathrm{arccos}$ on $[-1,1]$. | ||
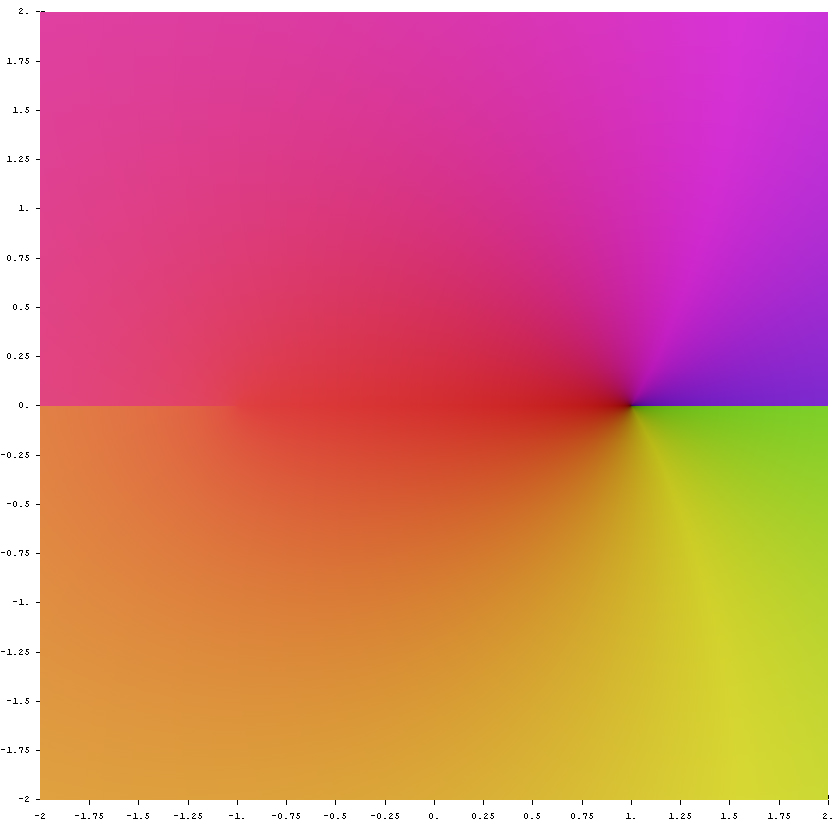
| + | File:Complex arccos.jpg|Domain coloring of analytic continuation to $\mathbb{C}$. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
=Properties= | =Properties= | ||
| − | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed | + | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> |
<strong>Proposition:</strong> | <strong>Proposition:</strong> | ||
$$\dfrac{d}{dz} \mathrm{arccos}(z) = -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1-z^2}}$$ | $$\dfrac{d}{dz} \mathrm{arccos}(z) = -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1-z^2}}$$ | ||
| Line 14: | Line 17: | ||
Hence substituting back in $y=\mathrm{arccos}(z)$ yields the formula <br /> | Hence substituting back in $y=\mathrm{arccos}(z)$ yields the formula <br /> | ||
$$\dfrac{d}{dz} \mathrm{arccos}(z) = -\dfrac{1}{\sin(\mathrm{arccos}(z))} = -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1-z^2}}.█$$ | $$\dfrac{d}{dz} \mathrm{arccos}(z) = -\dfrac{1}{\sin(\mathrm{arccos}(z))} = -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1-z^2}}.█$$ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed | + | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> |
<strong>Proposition:</strong> | <strong>Proposition:</strong> | ||
$$\int \mathrm{arccos}(z) dz = z\mathrm{arccos}(z)-\sqrt{1-z^2}+C$$ | $$\int \mathrm{arccos}(z) dz = z\mathrm{arccos}(z)-\sqrt{1-z^2}+C$$ | ||
| Line 27: | Line 28: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed | + | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> |
<strong>Proposition:</strong> | <strong>Proposition:</strong> | ||
$$\mathrm{arccos}(z)=\mathrm{arcsec} \left( \dfrac{1}{z} \right)$$ | $$\mathrm{arccos}(z)=\mathrm{arcsec} \left( \dfrac{1}{z} \right)$$ | ||
| Line 34: | Line 35: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | |||
=References= | =References= | ||
[http://mathworld.wolfram.com/InverseCosine.html Weisstein, Eric W. "Inverse Cosine." From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/InverseCosine.html] | [http://mathworld.wolfram.com/InverseCosine.html Weisstein, Eric W. "Inverse Cosine." From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/InverseCosine.html] | ||
Revision as of 03:16, 31 October 2014
The function $\mathrm{arccos} \colon [-1,1] \longrightarrow [0,\pi]$ is the inverse function of the cosine function.
Properties
Proposition: $$\dfrac{d}{dz} \mathrm{arccos}(z) = -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1-z^2}}$$
Proof: If $y=\mathrm{arccos}(z)$ then $\cos(y)=z$. Now use implicit differentiation with respect to $z$ to get
$$-\sin(y)y'=1.$$
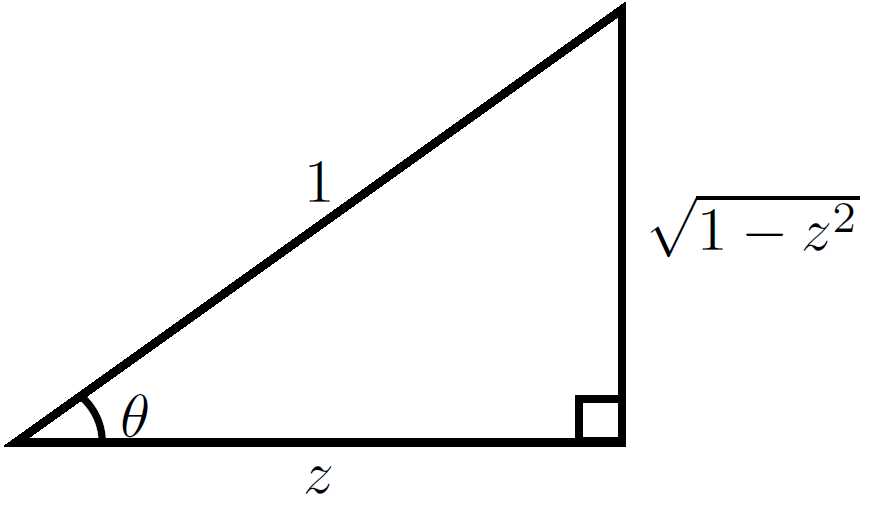
If we write $\theta=\mathrm{arccos}(z)$ then the following image shows that $\cos(\mathrm{arccos}(z))=\sqrt{1-z^2}$:
Hence substituting back in $y=\mathrm{arccos}(z)$ yields the formula
$$\dfrac{d}{dz} \mathrm{arccos}(z) = -\dfrac{1}{\sin(\mathrm{arccos}(z))} = -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1-z^2}}.█$$
Proposition: $$\int \mathrm{arccos}(z) dz = z\mathrm{arccos}(z)-\sqrt{1-z^2}+C$$
Proof: █
Proposition: $$\mathrm{arccos}(z)=\mathrm{arcsec} \left( \dfrac{1}{z} \right)$$
Proof: █