Difference between revisions of "Legendre P"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | The Legendre polynomials are [[orthogonal polynomials]] defined by the | + | The Legendre polynomials are [[orthogonal polynomials]] defined by the formula |
| − | $$P_n(x) = \dfrac{1}{2^ | + | $$P_n(x) = \dfrac{1}{2^n} \displaystyle\sum_{k=0}^n {n \choose k}^2 (x-1)^{n-k}(x+1)^k.$$ |
| + | |||
$$\begin{array}{ll} | $$\begin{array}{ll} | ||
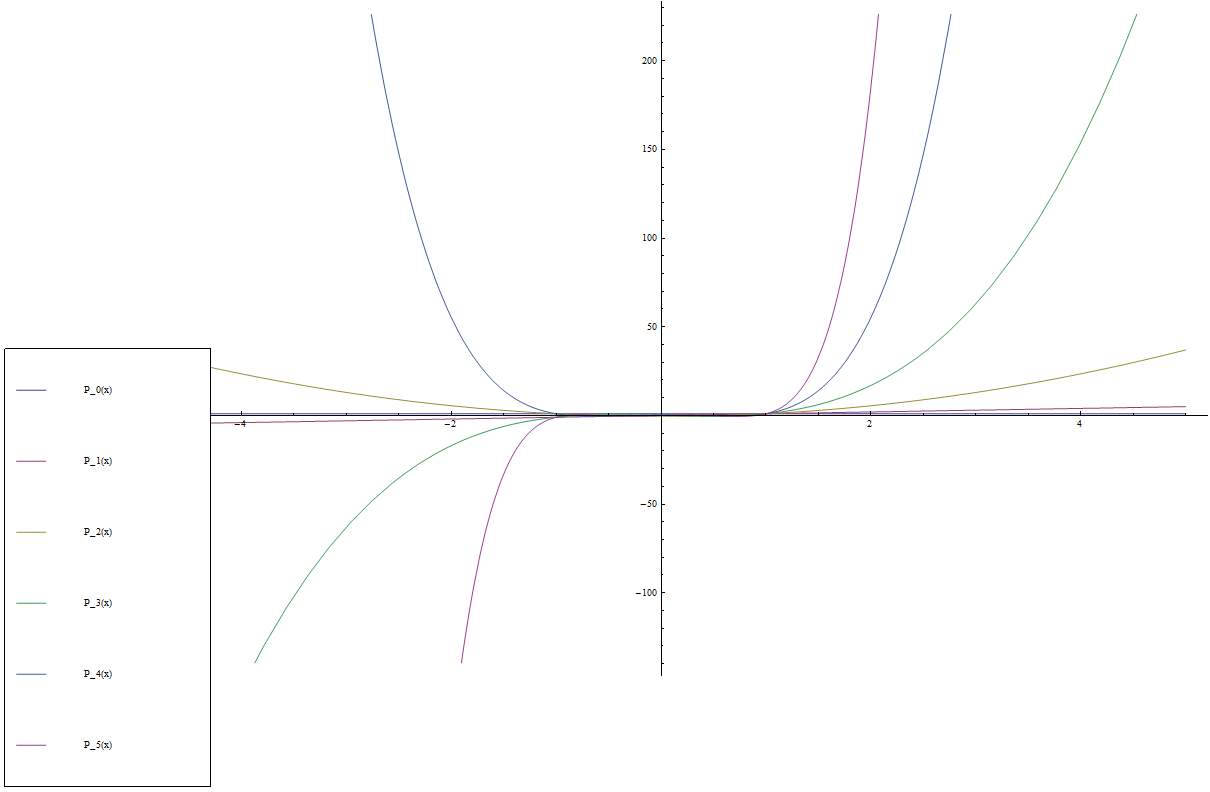
P_0(x) &= 1 \\ | P_0(x) &= 1 \\ | ||
| Line 6: | Line 7: | ||
P_2(x) &= \dfrac{1}{2}(3x^2-1) \\ | P_2(x) &= \dfrac{1}{2}(3x^2-1) \\ | ||
P_3(x) &= \dfrac{1}{2}(5x^3-3x) \\ | P_3(x) &= \dfrac{1}{2}(5x^3-3x) \\ | ||
| + | P_4(x) &= \dfrac{1}{8}(35x^4-30x^2+3) \\ | ||
| + | P_5(x) &= \dfrac{1}{8}(63x^5-70x^3+15x) \\ | ||
\vdots | \vdots | ||
\end{array}$$ | \end{array}$$ | ||
| Line 15: | Line 18: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | =Properties= | ||
| + | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | ||
| + | <strong>Theorem:</strong> The following formula holds: | ||
| + | $$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1-2xt+t^2}} = \displaystyle\sum_{k=0}^{\infty} P_n(x)t^n.$$ | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | <strong>Proof:</strong> █ | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | ||
| + | <strong>Theorem:</strong> ([[Rodrigues' formula]]) The following formula holds: | ||
| + | $$P_n(x)=\dfrac{1}{2^nn!}\dfrac{d^n}{dx^n} [(x^2-1)^n].$$ | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | <strong>Proof:</strong> █ | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | ||
| + | <strong>Theorem:</strong> (Orthogonality) The following formula holds: | ||
| + | $$\displaystyle\int_{-1}^1 P_m(x)P_n(x)dx = \dfrac{2}{2n+1} \delta_{mn},$$ | ||
| + | where $P_n$ denotes [[Legendre P|Legendre polynomials]] and $\delta$ denotes the [[Dirac delta]]. | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| + | <strong>Proof:</strong> █ | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
{{:Orthogonal polynomials footer}} | {{:Orthogonal polynomials footer}} | ||
Revision as of 20:27, 23 March 2015
The Legendre polynomials are orthogonal polynomials defined by the formula $$P_n(x) = \dfrac{1}{2^n} \displaystyle\sum_{k=0}^n {n \choose k}^2 (x-1)^{n-k}(x+1)^k.$$
$$\begin{array}{ll} P_0(x) &= 1 \\ P_1(x) &= x \\ P_2(x) &= \dfrac{1}{2}(3x^2-1) \\ P_3(x) &= \dfrac{1}{2}(5x^3-3x) \\ P_4(x) &= \dfrac{1}{8}(35x^4-30x^2+3) \\ P_5(x) &= \dfrac{1}{8}(63x^5-70x^3+15x) \\ \vdots \end{array}$$
Properties
Theorem: The following formula holds: $$\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1-2xt+t^2}} = \displaystyle\sum_{k=0}^{\infty} P_n(x)t^n.$$
Proof: █
Theorem: (Rodrigues' formula) The following formula holds: $$P_n(x)=\dfrac{1}{2^nn!}\dfrac{d^n}{dx^n} [(x^2-1)^n].$$
Proof: █
Theorem: (Orthogonality) The following formula holds: $$\displaystyle\int_{-1}^1 P_m(x)P_n(x)dx = \dfrac{2}{2n+1} \delta_{mn},$$ where $P_n$ denotes Legendre polynomials and $\delta$ denotes the Dirac delta.
Proof: █