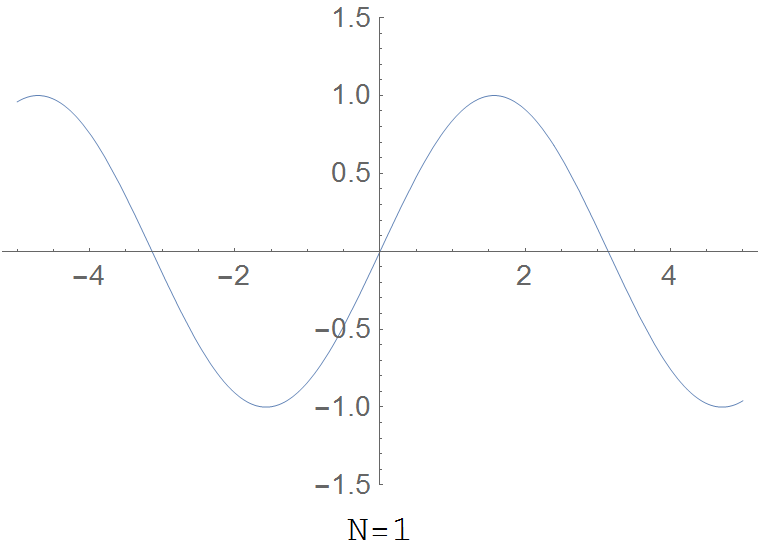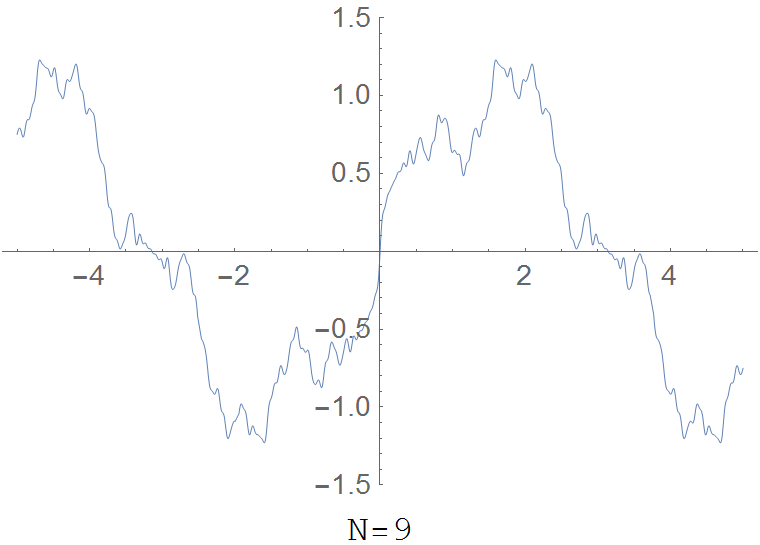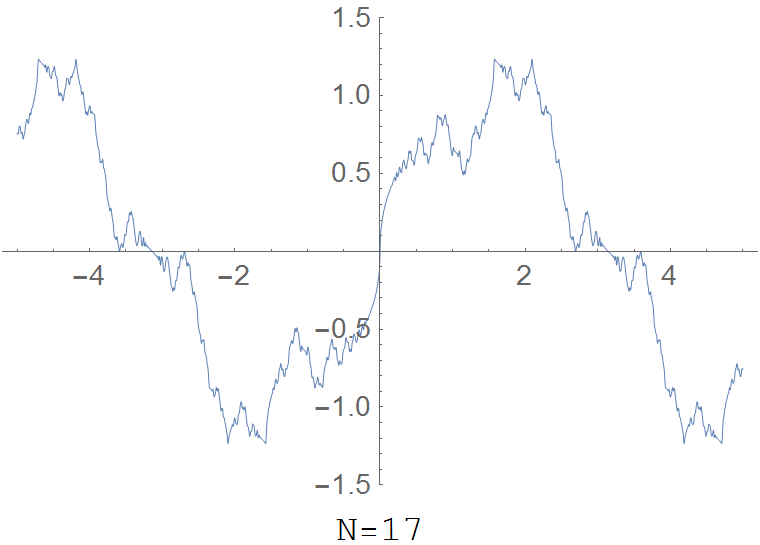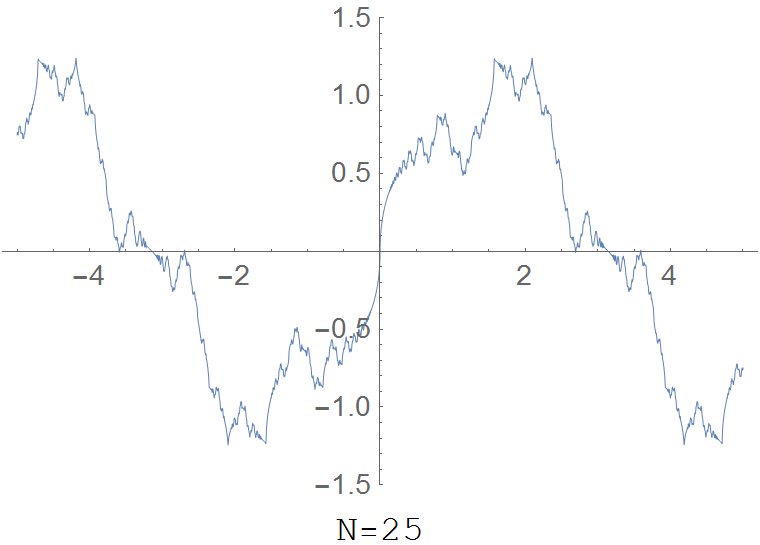Difference between revisions of "Riemann function"
From specialfunctionswiki
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
$$R(x)=\displaystyle\sum_{k=1}^{\infty} \dfrac{\sin(k^2 x)}{k^2}.$$ | $$R(x)=\displaystyle\sum_{k=1}^{\infty} \dfrac{\sin(k^2 x)}{k^2}.$$ | ||
| − | The partial sum $R(x,N)=\displaystyle\sum_{k=1}^N \dfrac{\sin(k^2 x)}{k^2}$ for various values of $N$ | + | <div align="center"> |
| − | + | <gallery> | |
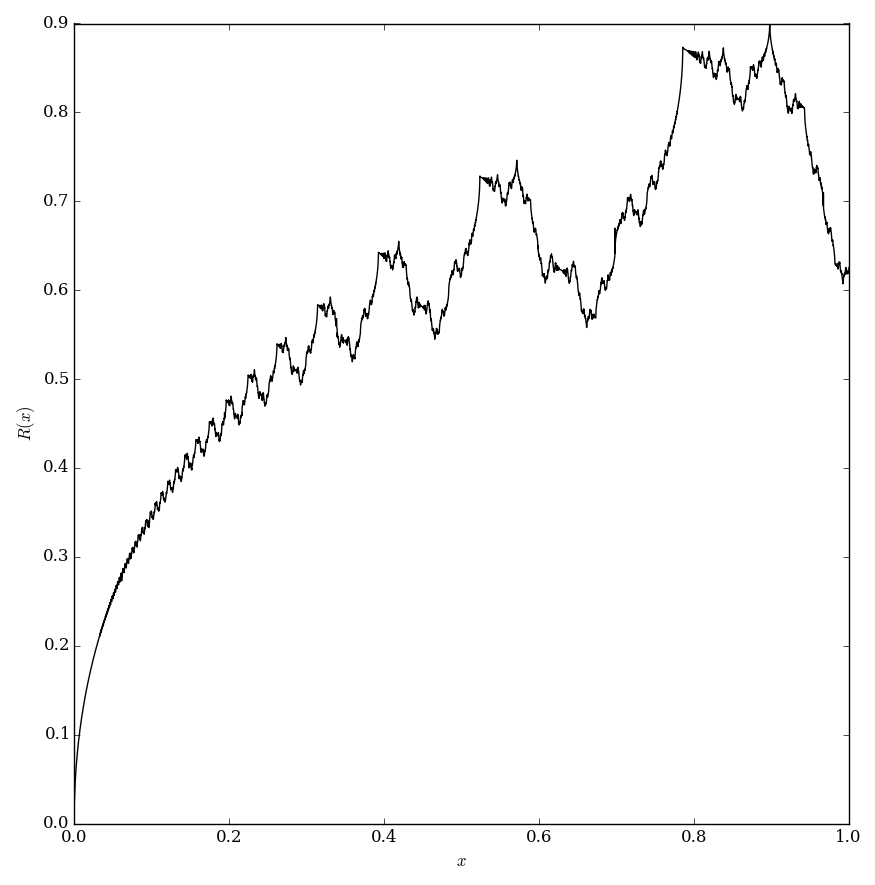
| + | File:Riemannplot.png|Plot of $R(x)$ on $[0,1]$. | ||
| + | File:Riemannfunction.gif|The partial sum $R(x,N)=\displaystyle\sum_{k=1}^N \dfrac{\sin(k^2 x)}{k^2}$ for various values of $N$. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
=Properties= | =Properties= | ||
Revision as of 16:48, 27 January 2016
The Riemann function is the function $R \colon \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ defined by $$R(x)=\displaystyle\sum_{k=1}^{\infty} \dfrac{\sin(k^2 x)}{k^2}.$$
Properties
Theorem: The Riemann function is is continuous.
Proof: █
Theorem: The Riemann function is nowhere differentiable except at points of the form $\pi \dfrac{2p+1}{2q+1}$ with $p,q \in \mathbb{Z}$.
Proof: █