Difference between revisions of "Prime counting"
From specialfunctionswiki
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
[http://people.mpim-bonn.mpg.de/zagier/files/doi/10.2307/2975232/fulltext.pdf Newman's short proof of the prime number theorem] | [http://people.mpim-bonn.mpg.de/zagier/files/doi/10.2307/2975232/fulltext.pdf Newman's short proof of the prime number theorem] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:SpecialFunction]] | ||
Revision as of 18:49, 24 May 2016
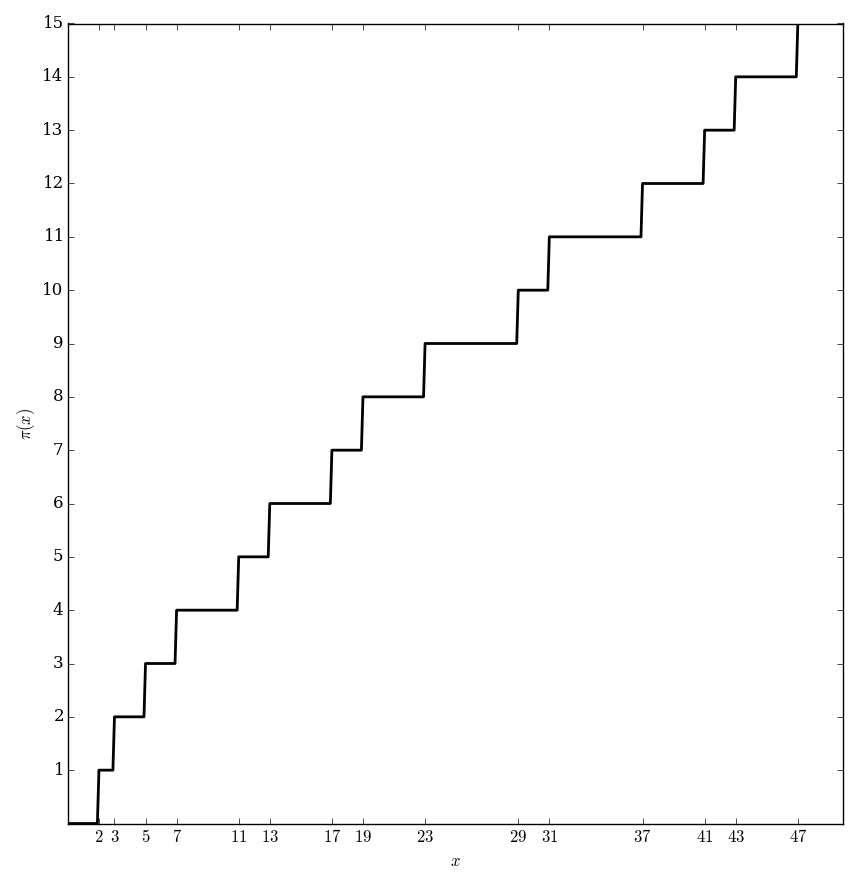
The prime counting function $\pi \colon \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{Z}^+$ is defined by the formula $$\pi(x) = \{\mathrm{number \hspace{2pt} of \hspace{2pt} primes} \leq x \}.$$
Contents
Properties
Theorem
The function $\pi(x)$ obeys the formula $$\lim_{x \rightarrow \infty} \dfrac{\pi(x)}{\frac{x}{\log(x)}}=1,$$ where $\pi$ denotes the prime counting function and $\log$ denotes the logarithm.
Proof
References
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\lim_{x \rightarrow \infty} \dfrac{\pi(x)}{\mathrm{li}(x)}=1,$$ where $\pi$ denotes the prime counting function and $\mathrm{li}$ denotes the logarithmic integral.