Difference between revisions of "Anger function"
(→See Also) |
(→See Also) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
=See Also= | =See Also= | ||
| − | [[Bessel J]] | + | [[Bessel J]]<br /> |
[[Weber function]] | [[Weber function]] | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
[http://dualaud.net/specialfunctionswiki/abramowitz_and_stegun-1.03/page_498.htm Abramowitz and Stegun]<br /> | [http://dualaud.net/specialfunctionswiki/abramowitz_and_stegun-1.03/page_498.htm Abramowitz and Stegun]<br /> | ||
Revision as of 17:01, 23 May 2016
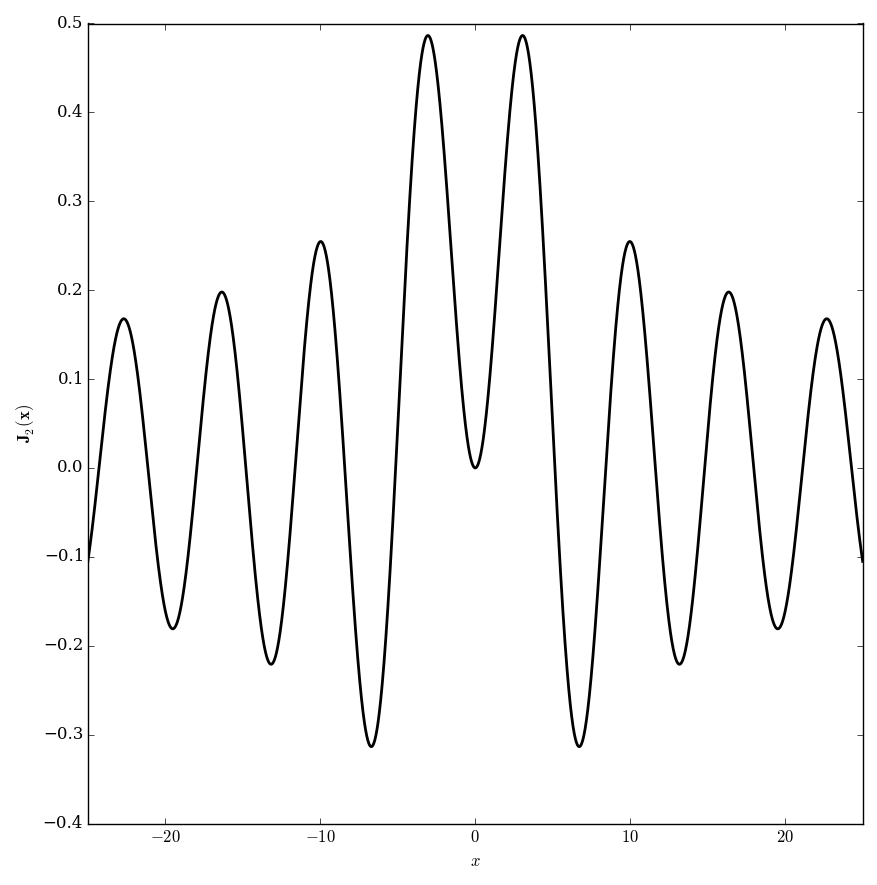
The Anger function is defined by $$\mathbf{J}_{\nu}(z) = \dfrac{1}{\pi} \displaystyle\int_0^{\pi} \cos(\nu \theta - z \sin(\theta)) \mathrm{d}\theta.$$
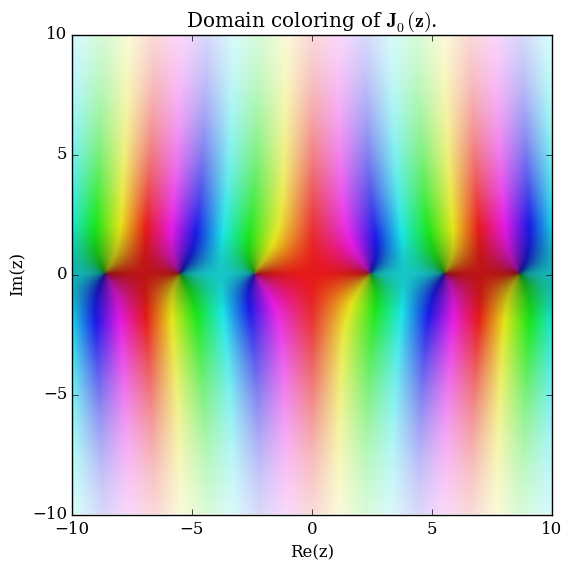
Domain coloring of $\mathbf{J}_0$.
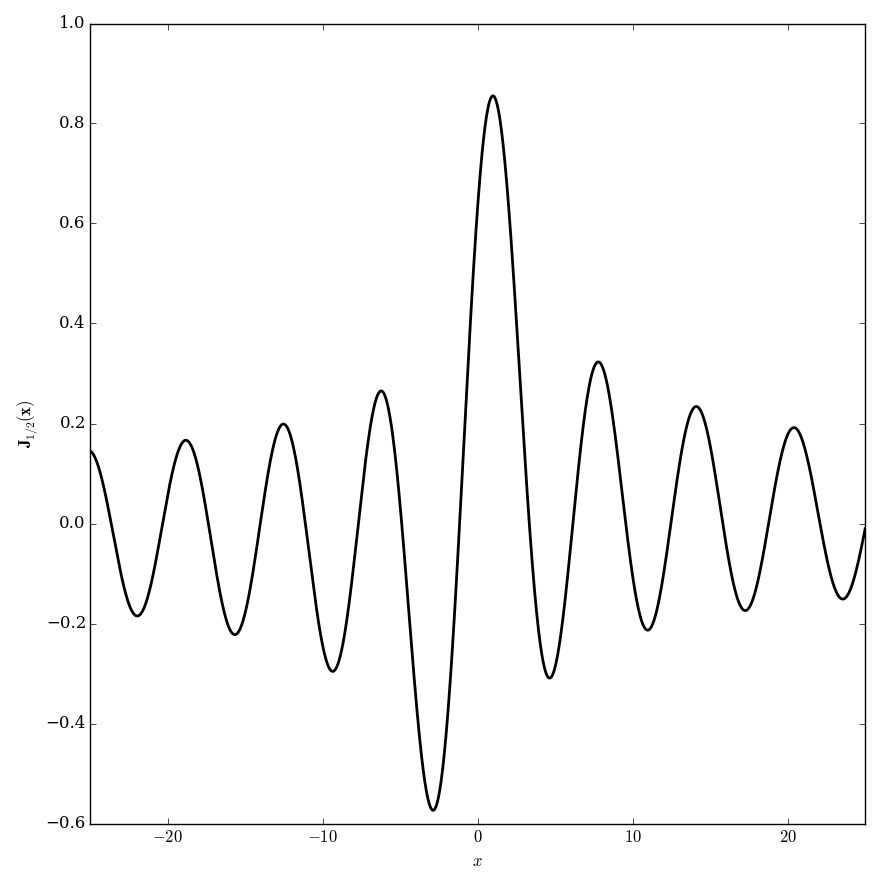
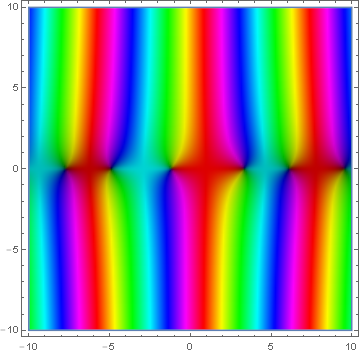
Domain coloring of analytic continuation of $\mathbf{J}_{\frac{1}{2}}$.
Contents
Properties
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\textbf{J}_{\nu}(0)=\dfrac{\sin(\pi \nu)}{\pi \nu},$$ where $\textbf{J}_{\nu}$ denotes an Anger function, $\sin$ denotes the sine, and $\pi$ denotes pi.
Proof
References
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\textbf{J}_{\nu-1}(z)+\textbf{J}_{\nu+1}(z)=\dfrac{2\nu}{z}\textbf{J}_{\nu}(z)-\dfrac{2}{\pi z}\sin(\pi \nu),$$ where $\textbf{J}_{\nu}$ denote the Anger function, $\pi$ denotes pi, and $\sin$ denotes sine.
Proof
References
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$2 \mathbf{J}_{\nu}'(z)=\mathbf{J}_{\nu-1}(z)-\mathbf{J}_{\nu+1}(z),$$ where $\mathbf{J}_{\nu}$ denotes the Anger function.
Proof
References
Theorem
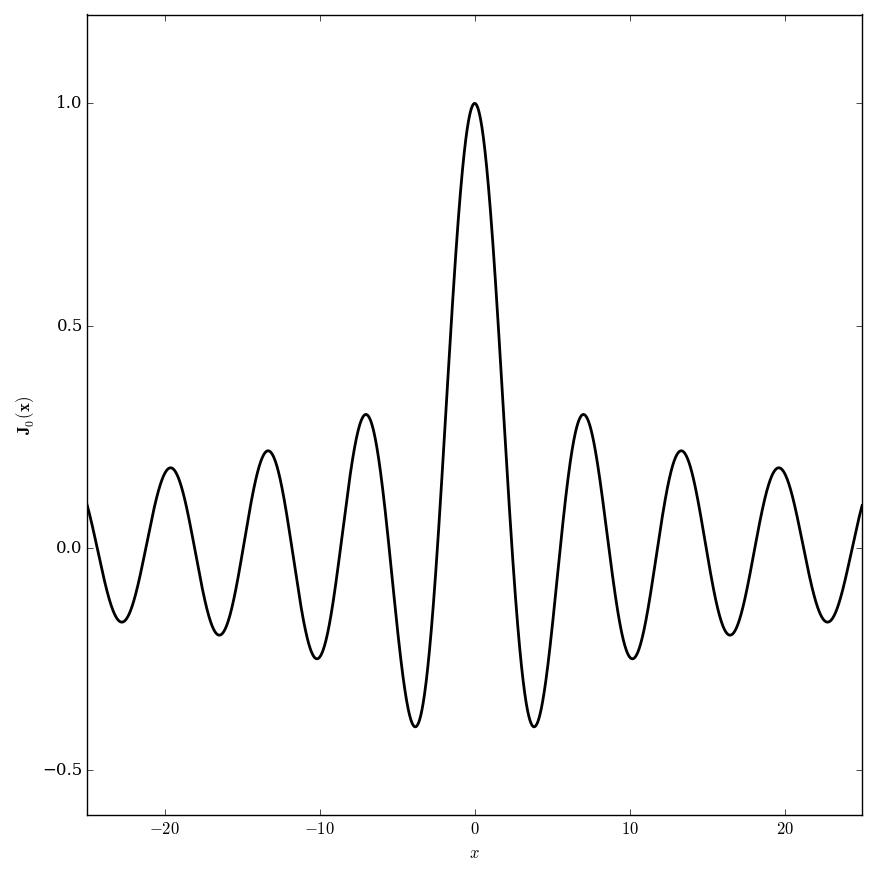
The following formula holds for integer $n$: $$\mathbf{J}_n(z)=J_n(z),$$ where $\mathbf{J}_n$ denotes an Anger function and $J_n$ denotes a Bessel function of the first kind.
Proof
References
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\sin(\nu \pi)\mathbf{E}_{\nu}(z)=\mathbf{J}_{-\nu}(z)-\cos(\nu \pi)\mathbf{J}_{\nu}(z),$$ where $\mathbf{E}_{\nu}$ denotes a Weber function and $\mathbf{J}_{\nu}$ denotes an Anger function.
Proof
References
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): 12.3.5
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\sin(\nu\pi)\mathbf{J}_{\nu}(z)=\cos(\nu \pi)\mathbf{E}_{\nu}(z)-\mathbf{E}_{-\nu}(z),$$ where $\mathbf{J}_{\nu}$ denotes an Anger function and $\mathbf{E}_{\nu}$ denotes a Weber function.
Proof
References
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): 12.3.4