Difference between revisions of "Arcsin"
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
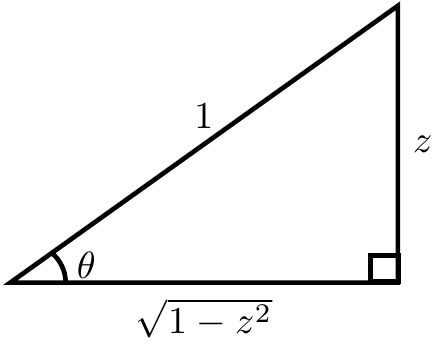
The following image shows that $\cos(\mathrm{arcsin}(z))=\sqrt{1-z^2}$: | The following image shows that $\cos(\mathrm{arcsin}(z))=\sqrt{1-z^2}$: | ||
[[File:Cos(arcsin(z)).png|200px|center]] | [[File:Cos(arcsin(z)).png|200px|center]] | ||
| − | $$\dfrac{d}{dz} \mathrm{arcsin(z)} = \dfrac{1}{\cos(\mathrm{arcsin(z)})} = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1-z^2}}. █ $$ | + | Hence substituting back in $\theta=\mathrm{arccos}(z)$ yields the formula |
| + | $$\dfrac{d}{dz} \mathrm{arcsin(z)} = \dfrac{1}{\cos(\mathrm{arcsin(z)})} = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1-z^2}}. █$$ | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 05:28, 31 October 2014
The function $\mathrm{arcsin} \colon [-1,1] \rightarrow \left[ -\frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2} \right]$ is the inverse function of the sine function.
- Arcsin.png
Graph of $\mathrm{arcsin}$ on $[-1,1]$.
- Complex arcsin.jpg
Properties
Proposition: $$\dfrac{d}{dz} \mathrm{arcsin(z)} = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1-z^2}}$$
Proof: If $\theta=\mathrm{arcsin}(z)$ then $\sin(\theta)=z$. Now use implicit differentiation with respect to $z$ to get $$\cos(\theta)\theta'=1.$$ The following image shows that $\cos(\mathrm{arcsin}(z))=\sqrt{1-z^2}$:
Hence substituting back in $\theta=\mathrm{arccos}(z)$ yields the formula $$\dfrac{d}{dz} \mathrm{arcsin(z)} = \dfrac{1}{\cos(\mathrm{arcsin(z)})} = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1-z^2}}. █$$
Proposition: $$\int \mathrm{arcsin}(z) dz = \sqrt{1-z^2}+z\mathrm{arcsin}(z)+C$$
Proof: █
Proposition: $$\mathrm{arcsin}(z) = \mathrm{arccsc}\left( \dfrac{1}{z} \right)$$
Proof: █
Proposition: $$\mathrm{arcsin}(z)=\sum_{k=0}^{\infty} \dfrac{\left(\frac{1}{2} \right)_n}{(2n+1)n!}x^{2n+1}$$
Proof: █