Difference between revisions of "Sinc"
(→Videos) |
|||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
[https://youtu.be/3Sjn3XLo5XE?t=306 Discrete-Time Signals and Systems Introduction (4/6): Special Functions]<br /> | [https://youtu.be/3Sjn3XLo5XE?t=306 Discrete-Time Signals and Systems Introduction (4/6): Special Functions]<br /> | ||
[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xx2AQz_ZyC0 Integrating the sinc function]<br /> | [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xx2AQz_ZyC0 Integrating the sinc function]<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>{{:*-c functions footer}}</center> | ||
Revision as of 23:04, 19 May 2015
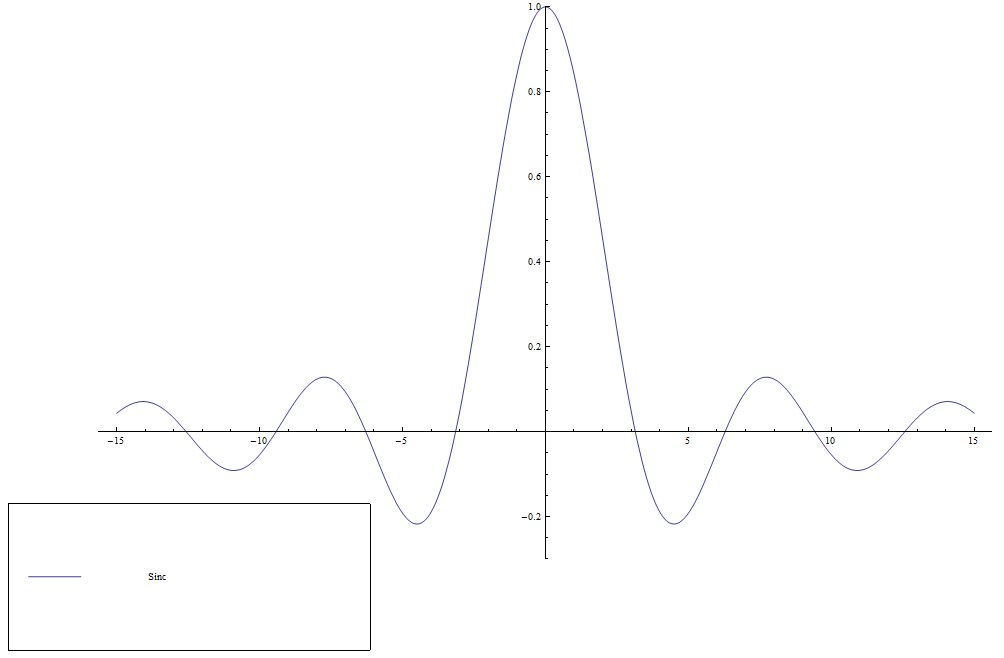
The $\mathrm{sinc}$ function (sometimes called the unnormalized $\mathrm{sinc}$ function) is defined by $$\mathrm{sinc}(x) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \dfrac{\sin x}{x} &; x \neq 0 \\ 1 &; x=0. \end{array} \right.$$ It appears in the definition of the Sine integral function.
- Complex sinc.png
Domain coloring of analytic continuation of $\mathrm{sinc}$ on $[-15,15] \times [-15,15] \subset \mathbb{C}$.
Properties
Theorem: The following formula holds: $$\mathrm{sinc}(x)=\displaystyle\prod_{k=1}^{\infty} \cos \left( \dfrac{x}{2^k} \right).$$
Proof: █
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\displaystyle\sum_{k=1}^{\infty} \mathrm{sinc}(k) = \dfrac{\pi-1}{2},$$ where $\mathrm{sinc}$ denotes the $\mathrm{sinc}$ function and $\pi$ denotes pi.
Proof
References
Theorem: The following formula holds: $$\displaystyle\sum_{k=1}^{\infty} (-1)^{k+1}\mathrm{sinc}(k)=\dfrac{1}{2}.$$
Proof: █
Videos
Infinite Product Evaluation with the Sinc Function
(The Sinc Function) Inverse Fourier Transform of Sinc & Fourier Transform of Sinc
Fourier Transform of a Sinc Function (or Inverse Fourier Transform of a Low Pass Filter)
Discrete-Time Signals and Systems Introduction (4/6): Special Functions
Integrating the sinc function