Difference between revisions of "Airy Bi"
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
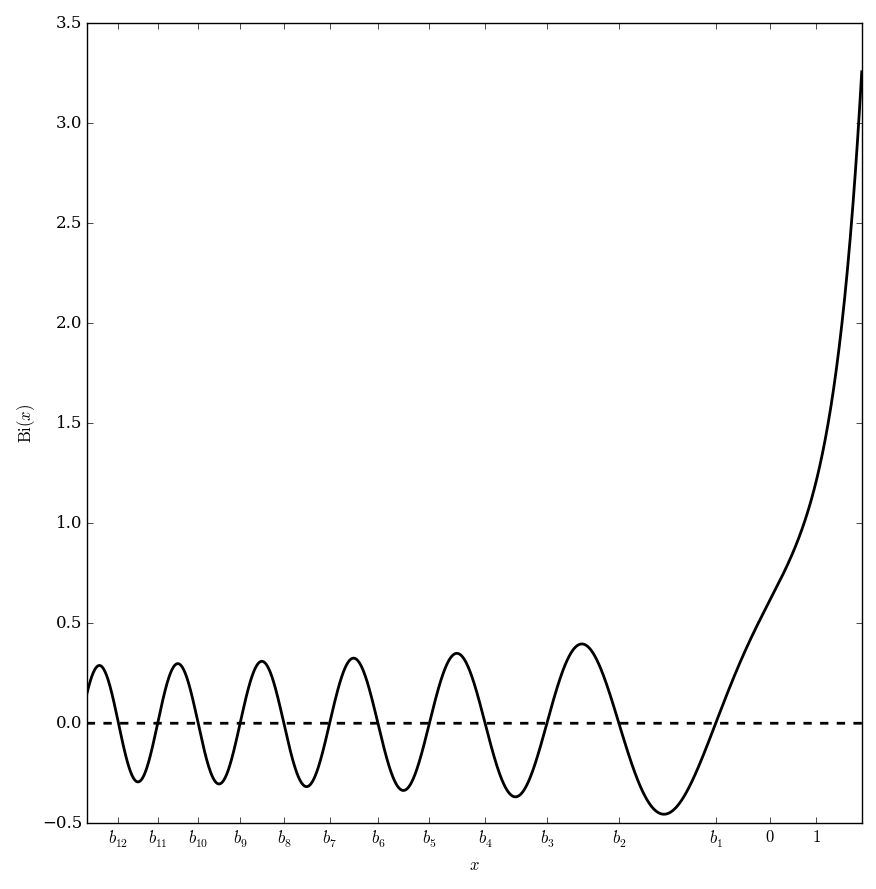
File:Airybiplot.png|Aairy $\mathrm{Bi}$ function. | File:Airybiplot.png|Aairy $\mathrm{Bi}$ function. | ||
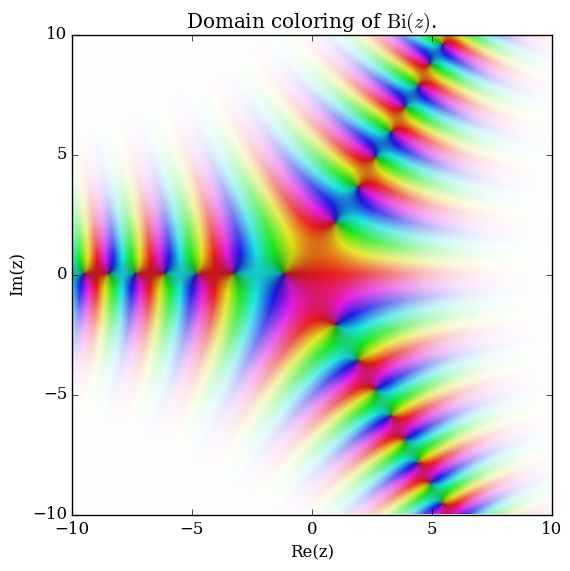
| − | File: | + | File:Complexairybiplot.png|[[Domain coloring]] of $\mathrm{Bi}$. |
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 07:47, 16 May 2016
The Airy function $\mathrm{Bi}$ (sometimes called the "Bairy function") is a solution of the Airy differential equation $$y(z)-zy(z)=0,$$ which is linearly independent from the Airy Ai function.
Domain coloring of $\mathrm{Bi}$.
Contents
Properties
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\mathrm{Bi}(z)=\sqrt{\dfrac{z}{3}} \left( I_{\frac{1}{3}}\left(\frac{2}{3}x^{\frac{3}{2}} \right) + I_{-\frac{1}{3}} \left( \frac{2}{3} x^{\frac{3}{2}} \right) \right),$$ where $\mathrm{Bi}$ denotes the Airy Bi function and $I_{\nu}$ denotes the modified Bessel $I$.
Proof
References
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\mathrm{Gi}(x)=\mathrm{Bi}(x)\displaystyle\int_x^{\infty} \mathrm{Ai}(t)\mathrm{d}t + \mathrm{Ai}(x)\displaystyle\int_0^x \mathrm{Bi}(t) \mathrm{d}t,$$ where $\mathrm{Gi}$ denotes the Scorer Gi function, $\mathrm{Ai}$ denotes the Airy Ai function, and $\mathrm{Bi}$ denotes the Airy Bi function.
Proof
References
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\mathrm{Hi}(x)=\mathrm{Bi}(x)\displaystyle\int_{-\infty}^x \mathrm{Ai}(t) \mathrm{d}t - \mathrm{Ai}(x)\displaystyle\int_{-\infty}^x \mathrm{Bi}(t)\mathrm{d}t,$$ where $\mathrm{Hi}$ denotes the Scorer Hi function, $\mathrm{Ai}$ denotes the Airy Ai function, and $\mathrm{Bi}$ denotes the Airy Bi function.
Proof
References
Videos
Airy differential equation
Series solution of ode: Airy's equation
Leading Tsunami wave reaching the shore
References
The mathematics of rainbows
Tables of Weyl Fractional Integrals for the Airy Function
Special Functions: An Introduction to the Classical Functions of Mathematical Physics
Airy function zeros