Difference between revisions of "Prime counting"
From specialfunctionswiki
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<div align="center"> | <div align="center"> | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
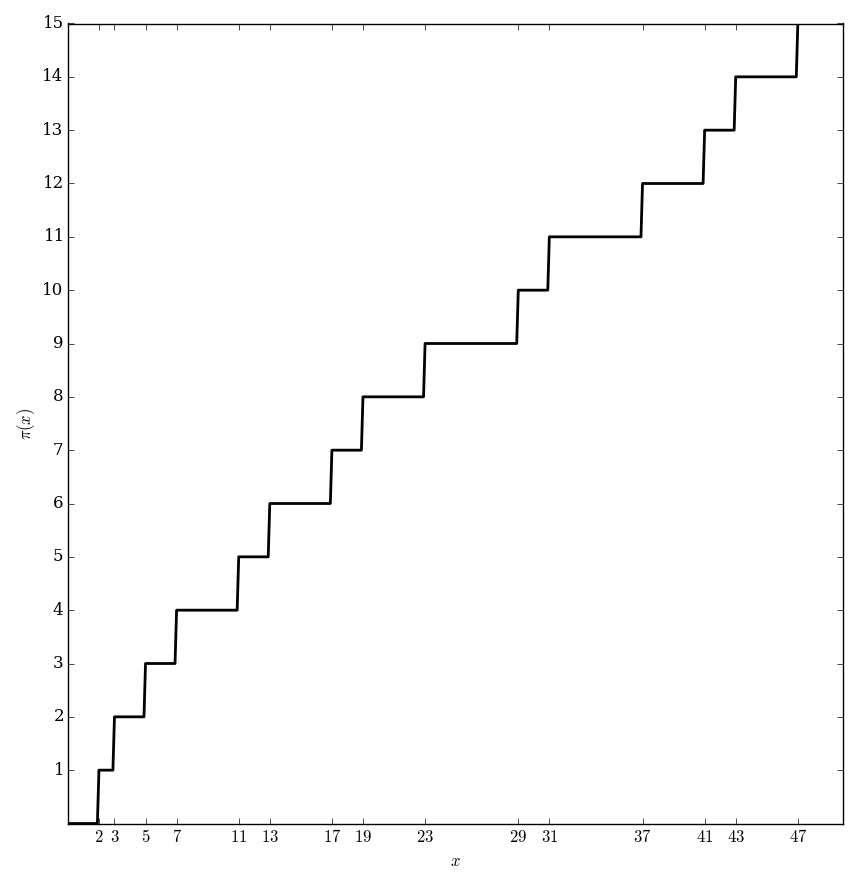
| − | File: | + | File:Primecountingplot.png|Graph of $\pi(x)$. |
| − | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 20:03, 16 May 2016
The prime counting function $\pi \colon \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{Z}^+$ is defined by the formula $$\pi(x) = \{\mathrm{number \hspace{2pt} of \hspace{2pt} primes} \leq x \}.$$
Contents
Properties
Theorem
The function $\pi(x)$ obeys the formula $$\lim_{x \rightarrow \infty} \dfrac{\pi(x)}{\frac{x}{\log(x)}}=1,$$ where $\pi$ denotes the prime counting function and $\log$ denotes the logarithm.
Proof
References
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\lim_{x \rightarrow \infty} \dfrac{\pi(x)}{\mathrm{li}(x)}=1,$$ where $\pi$ denotes the prime counting function and $\mathrm{li}$ denotes the logarithmic integral.