Difference between revisions of "Riemann zeta"
(→External links) |
|||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
*[http://empslocal.ex.ac.uk/people/staff/mrwatkin//zeta/devlin.pdf How Euler discovered the zeta function] | *[http://empslocal.ex.ac.uk/people/staff/mrwatkin//zeta/devlin.pdf How Euler discovered the zeta function] | ||
*[http://www.dtc.umn.edu/~odlyzko/zeta_tables/ Andrew Odlyzko: Tables of zeros of the Riemann zeta function] | *[http://www.dtc.umn.edu/~odlyzko/zeta_tables/ Andrew Odlyzko: Tables of zeros of the Riemann zeta function] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:SpecialFunction]] | ||
Revision as of 18:49, 24 May 2016
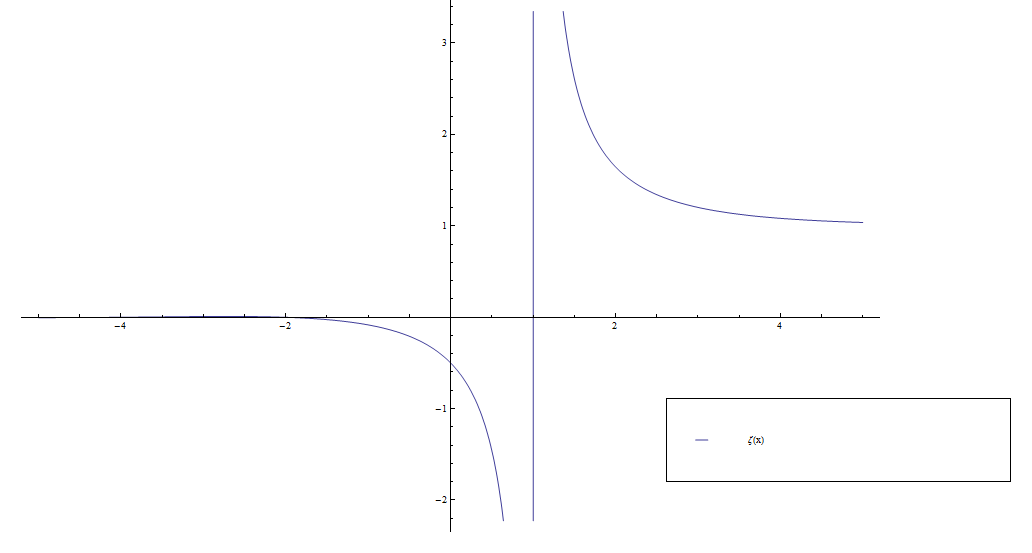
Consider the function $\zeta$ defined by the series $$\zeta(z) = \displaystyle\sum_{n=1}^{\infty} \dfrac{1}{n^z}.$$
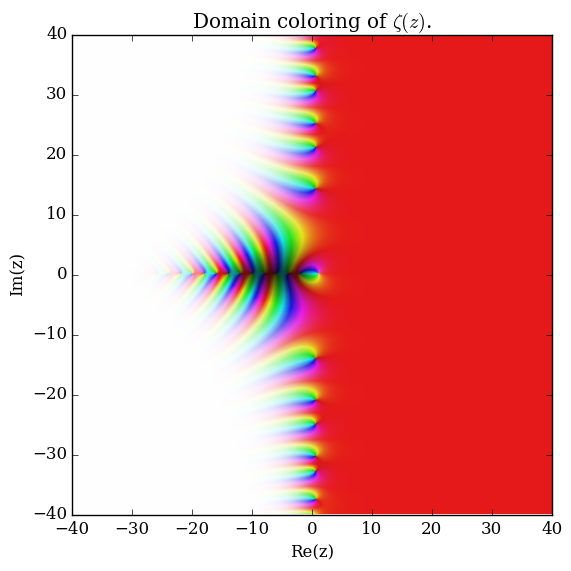
Domain coloring of $\zeta$.
Contents
Properties
Proposition: If $\mathrm{Re} \hspace{2pt} z > 1$, then the series defining $\zeta(z)$ converges.
Proof: █
Theorem
The following formula holds for $\mathrm{Re}(z)>1$: $$\zeta(z)=\displaystyle\prod_{p \mathrm{\hspace{2pt} prime}} \dfrac{1}{1-p^{-z}},$$ where $\zeta$ denotes Riemann zeta.
Proof
References
- 1930: Edward Charles Titchmarsh: The Zeta-Function of Riemann ... (previous) ... (next): § Introduction $(2)$
- 1953: Harry Bateman: Higher Transcendental Functions Volume III ... (previous) ... (next): pg. $170$
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): $23.2.2$
Proposition: Let $n$ be a positive integer. Then $$\zeta(2n)=(-1)^{n+1}\dfrac{B_{2n}(2\pi)^{2n}}{2(2n)!},$$ where $B_n$ denotes the Bernoulli numbers.
Proof: █
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$P(z)=\displaystyle\sum_{k=1}^{\infty} \dfrac{\mu(k)}{k} \log \zeta(kz),$$ where $P$ denotes the Prime zeta function, $\mu$ denotes the Möbius function, $\log$ denotes the logarithm, and $\zeta$ denotes the Riemann zeta function.
Proof
References
Videos
Riemann Zeta function playlist
External links
- 15 Videos about the Riemann $\zeta$ function
- English translation of Riemann's paper "On the number of prime numbers less than a given quantity"
- Evaluating $\zeta(2)$
- The Riemann Hypothesis: How to make $1 Million Without Getting Out of Bed
- The Riemann Hypothesis: FAQ and resources
- How Euler discovered the zeta function
- Andrew Odlyzko: Tables of zeros of the Riemann zeta function