Difference between revisions of "Exponential integral Ei"
From specialfunctionswiki
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
[[Exponential integral Ei series]]<br /> | [[Exponential integral Ei series]]<br /> | ||
[[Relationship between exponential integral Ei, cosine integral, and sine integral]]<br /> | [[Relationship between exponential integral Ei, cosine integral, and sine integral]]<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =See Also= | ||
| + | [[Exponential integral E]] | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | + | * {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev=Exponential integral E|next=Logarithmic integral}}: $5.1.2$ | |
[http://gdz.sub.uni-goettingen.de/dms/load/img/?PID=PPN600494829_0018%7CLOG_0048 On certain definite integrals involving the exponential-integral - J.W.L. Glaisher] | [http://gdz.sub.uni-goettingen.de/dms/load/img/?PID=PPN600494829_0018%7CLOG_0048 On certain definite integrals involving the exponential-integral - J.W.L. Glaisher] | ||
Revision as of 18:39, 7 August 2016
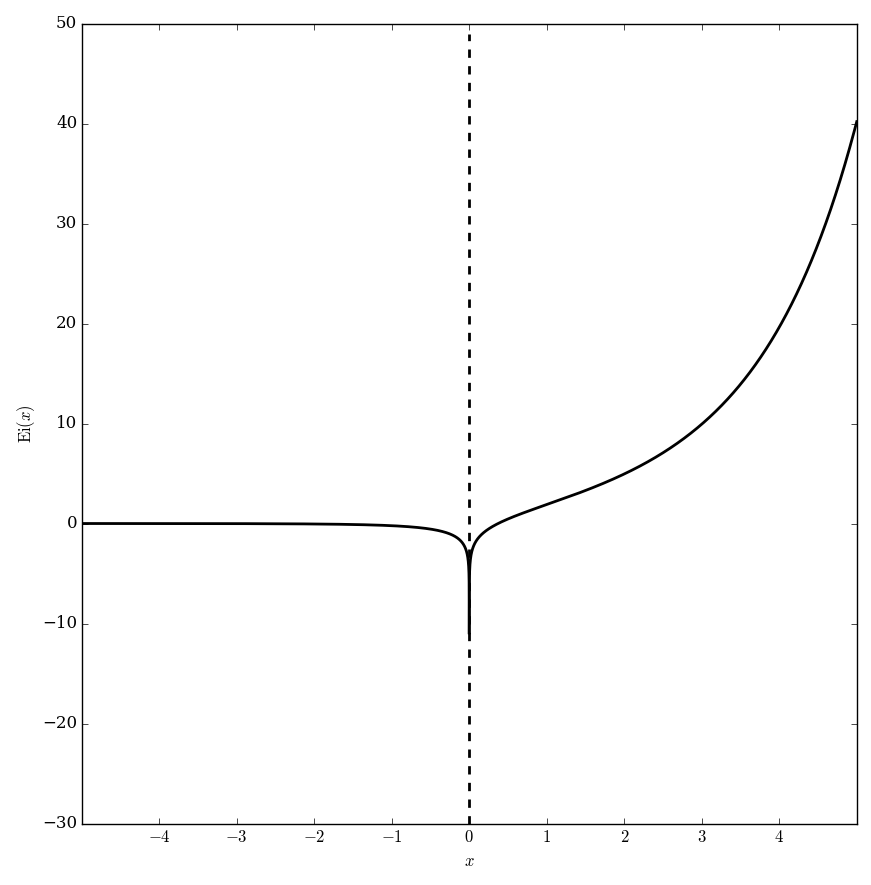
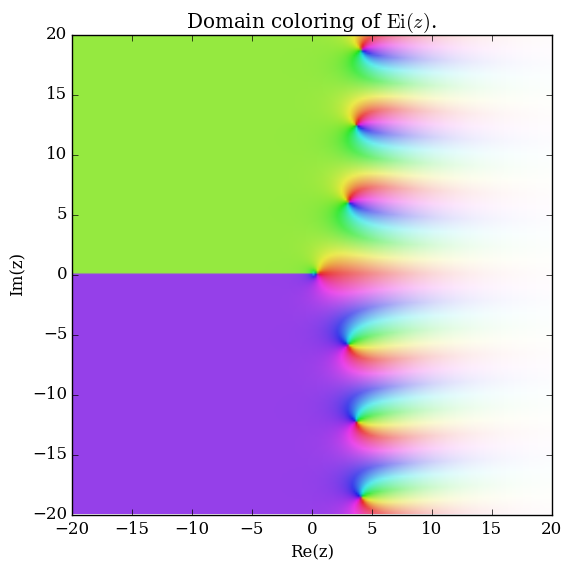
The exponential integral $\mathrm{Ei}$ is defined by $$\mathrm{Ei}(z) = \int_{-\infty}^x \dfrac{e^t}{t} \mathrm{d}t, \quad \left|\mathrm{arg}(-z) \right|<\pi.$$
Properties
Relationship between logarithmic integral and exponential integral
Exponential integral Ei series
Relationship between exponential integral Ei, cosine integral, and sine integral
See Also
References
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): $5.1.2$
On certain definite integrals involving the exponential-integral - J.W.L. Glaisher