Difference between revisions of "Inverse error function"
From specialfunctionswiki
(→Properties) |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
=Properties= | =Properties= | ||
| − | + | [[Derivative of inverse error function]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | ||
Revision as of 04:36, 16 September 2016
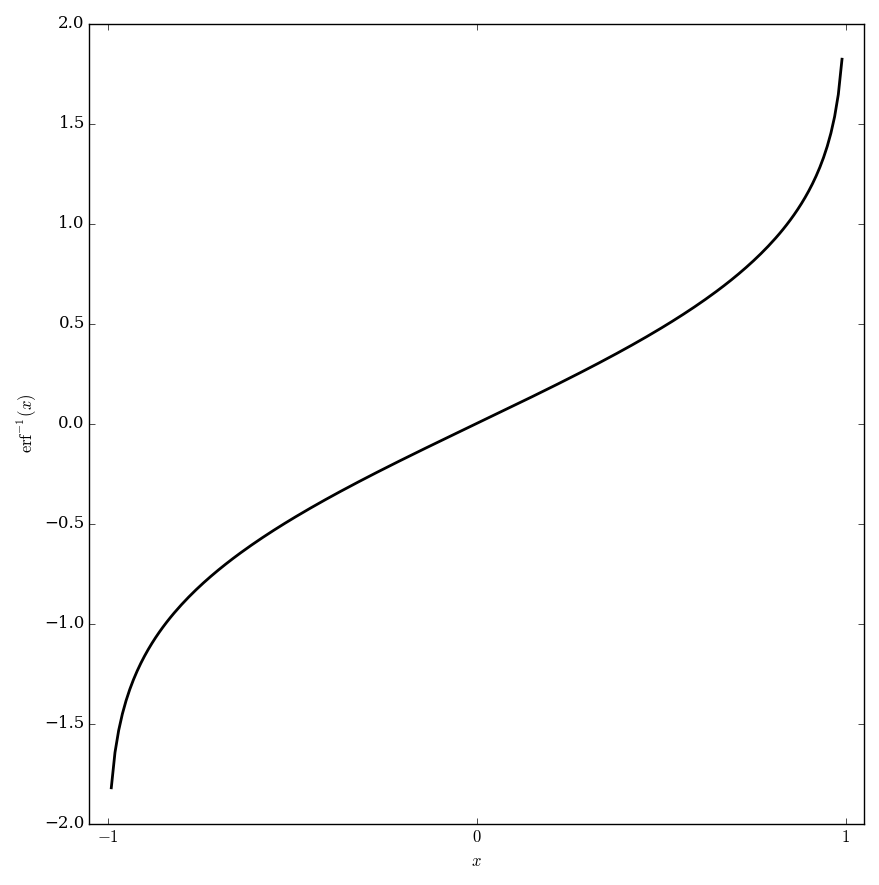
The inverse error function is the inverse function of the error function. We denote it by writing $\mathrm{erf}^{-1}$.
Properties
Derivative of inverse error function
Theorem: The following formula holds: $$\displaystyle\int \mathrm{erf}^{-1}(x) dx = -\dfrac{e^{-[\mathrm{erf}^{-1}(x)]^2}}{\sqrt{\pi}}.$$
Proof: █
Theorem: The following formula holds: $$\displaystyle\int_0^1 \mathrm{erf}^{-1}(x) dx=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{\pi}}.$$
Proof: █
Theorem: The following formula holds: $$\displaystyle\int_0^1 \log(\mathrm{erf}^{-1}(x)) dx = \left( \dfrac{\gamma}{2} + \log(2) \right),$$ where $\mathrm{erf}^{-1}$ denotes the inverse error function, $\log$ denotes the logarithm, and $\gamma$ denotes the Euler-Mascheroni constant.
Proof: █