Difference between revisions of "Arcsin"
(→Properties) |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
=Properties= | =Properties= | ||
| − | + | {{:Derivative of arcsin}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | ||
Revision as of 21:14, 15 May 2016
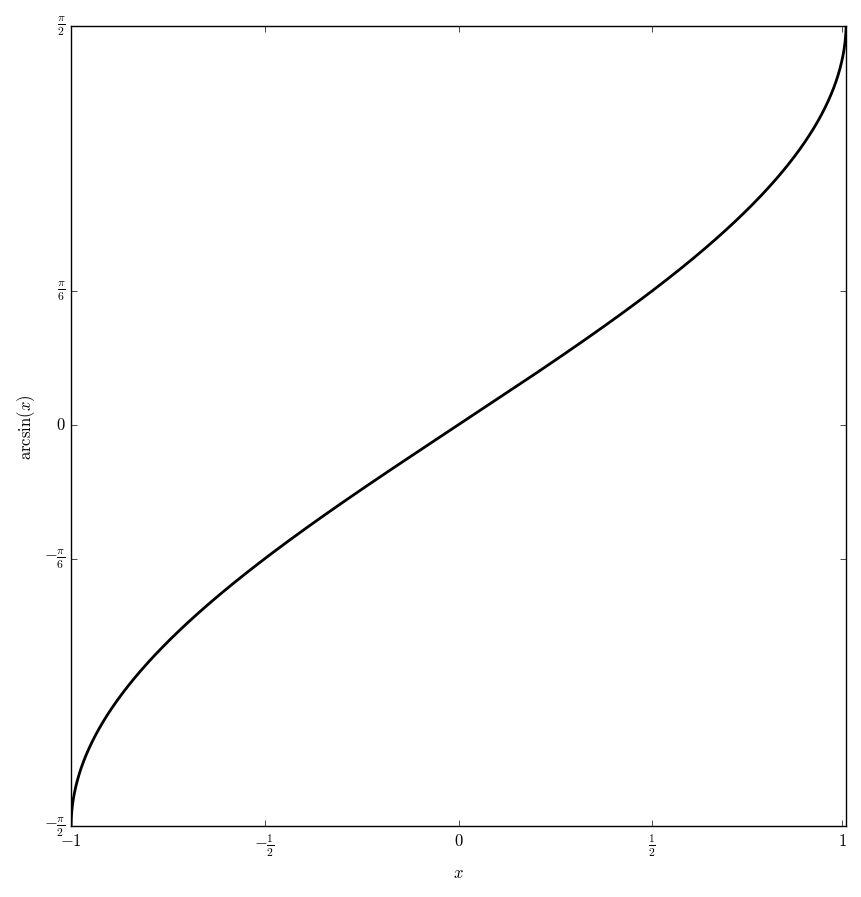
The function $\mathrm{arcsin} \colon [-1,1] \rightarrow \left[ -\frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2} \right]$ is the inverse function of the sine function.
- Complex arcsin.jpg
Domain coloring of analytic continuation $\mathrm{arcsin}$.
Properties
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\dfrac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d}z} \mathrm{arcsin(z)} = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1-z^2}},$$ where $\arcsin$ denotes the inverse sine function.
Proof
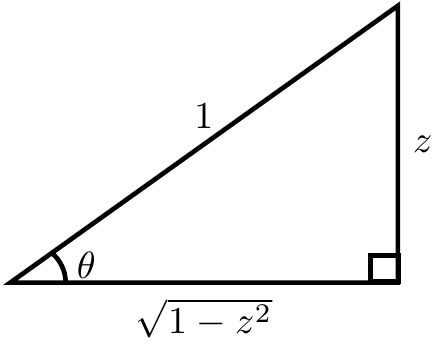
If $\theta=\mathrm{arcsin}(z)$ then $\sin(\theta)=z$. Now use implicit differentiation with respect to $z$ and the derivative of sine to get $$\cos(\theta)\theta'=1,$$ or equivalently $$\dfrac{\mathrm{d}\theta}{\mathrm{d}z} = \dfrac{1}{\cos(\theta)}.$$ The following image shows that $\cos(\mathrm{arcsin}(z))=\sqrt{1-z^2}$:
Hence substituting back in $\theta=\mathrm{arccos}(z)$ yields the formula $$\dfrac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d}z} \mathrm{arcsin(z)} = \dfrac{1}{\cos(\mathrm{arcsin(z)})} = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1-z^2}},$$ as was to be shown. █
References
Proposition: $\displaystyle\int \mathrm{arcsin}(z) dz = \sqrt{1-z^2}+z\mathrm{arcsin}(z)+C$
Proof: █
Proposition: $\mathrm{arcsin}(z) = \mathrm{arccsc}\left( \dfrac{1}{z} \right)$
Proof: █
Proposition: $\mathrm{arcsin}(z)=\displaystyle\sum_{k=0}^{\infty} \dfrac{\left(\frac{1}{2} \right)_n}{(2n+1)n!}x^{2n+1}$
Proof: █
Relationship between arcsin and hypergeometric 2F1
Videos
Inverse Trig Functions: Arcsin
Integrate x*arcsin(x)
What is arcsin(x)?
What is the inverse of arcsin(ln(x))?