Difference between revisions of "Gamma"
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
* {{BookReference|Einleitung in die Theorie der Gammafunktion und der Euler'schen Integrale|1895|Johann Heinrich Graf|prev=findme|next=findme}}: $\S 3 (15_a)$ | * {{BookReference|Einleitung in die Theorie der Gammafunktion und der Euler'schen Integrale|1895|Johann Heinrich Graf|prev=findme|next=findme}}: $\S 3 (15_a)$ | ||
* {{BookReference|A course of modern analysis|1920|Edmund Taylor Whittaker|author2=George Neville Watson|edpage=Third edition|prev=findme|next=Euler-Mascheroni constant}}: $\S 12 \cdot 1$ | * {{BookReference|A course of modern analysis|1920|Edmund Taylor Whittaker|author2=George Neville Watson|edpage=Third edition|prev=findme|next=Euler-Mascheroni constant}}: $\S 12 \cdot 1$ | ||
| − | * {{BookReference|Higher Transcendental Functions Volume I|1953| | + | * {{BookReference|Higher Transcendental Functions Volume I|1953|Arthur Erdélyi|author2=Wilhelm Magnus|author3=Fritz Oberhettinger|author4=Francesco G. Tricomi|next=Gamma(z) as integral of a power of log(1/t) for Re(z) greater than 0}}: $\S 1.1 (1)$ |
* {{BookReference|Special Functions of Mathematical Physics and Chemistry|1956|Ian N. Sneddon|prev=findme|next=Beta}}: $\S 5 (5.1)$ | * {{BookReference|Special Functions of Mathematical Physics and Chemistry|1956|Ian N. Sneddon|prev=findme|next=Beta}}: $\S 5 (5.1)$ | ||
* {{BookReference|Special Functions|1960|Earl David Rainville|prev=findme|next=findme}}: $15.(1)$ | * {{BookReference|Special Functions|1960|Earl David Rainville|prev=findme|next=findme}}: $15.(1)$ | ||
Revision as of 20:56, 3 March 2018
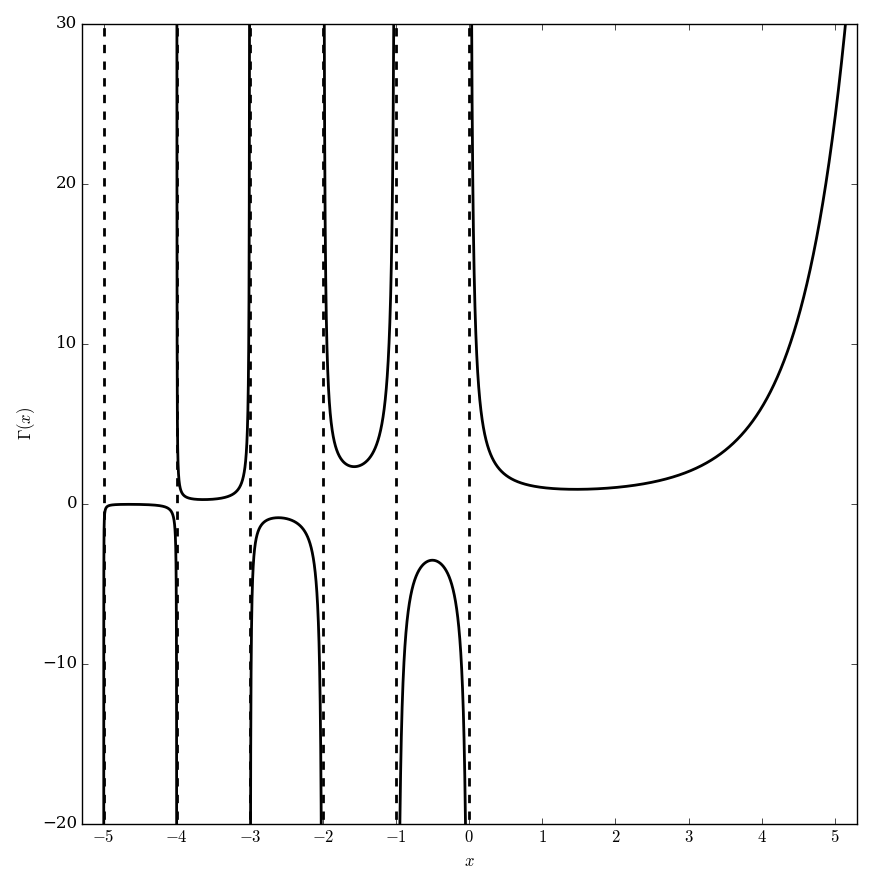
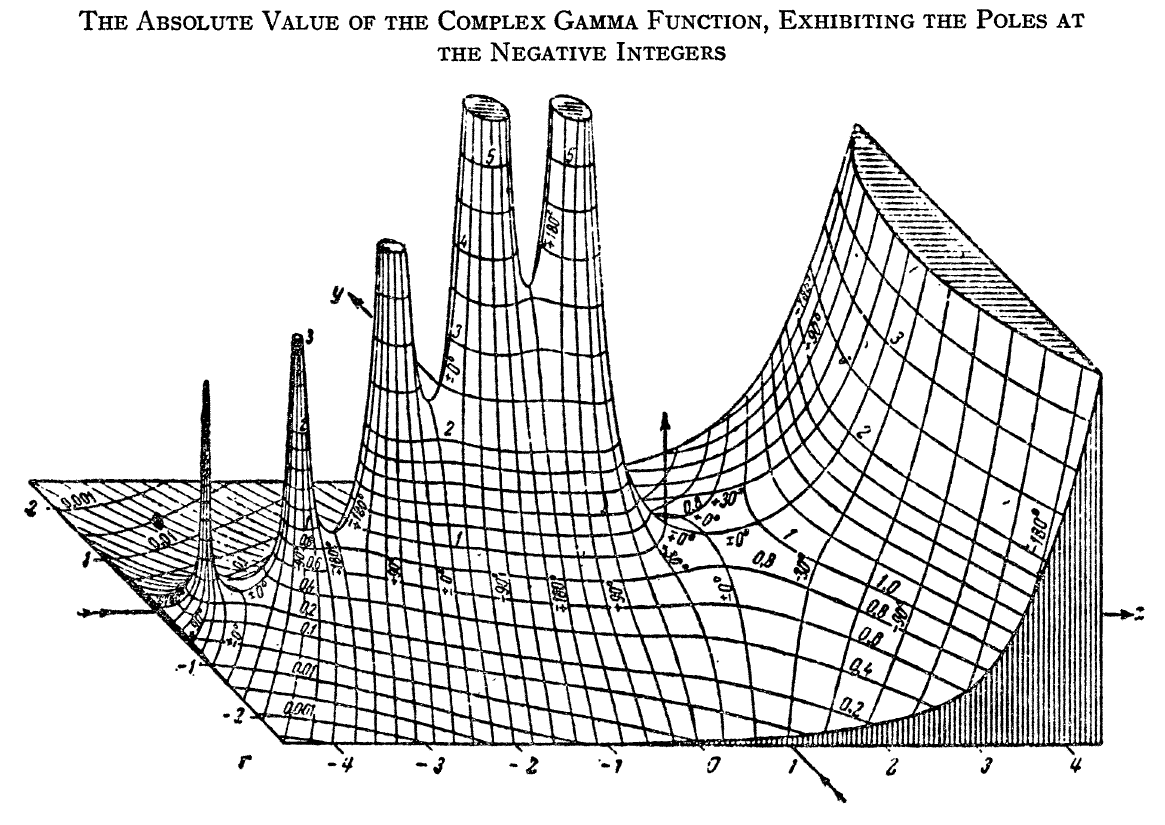
The gamma function $\Gamma \colon \mathbb{C} \setminus \{0,-1,-2,\ldots\} \rightarrow \mathbb{C}$ is the function initially defined for $\mathrm{Re}(z)>0$ by the integral by the formula $$\Gamma(z)=\displaystyle\int_0^{\infty} \xi^{z-1}e^{-\xi} \mathrm{d}\xi.$$ The analytic continuation of $\Gamma$ leads to a meromorphic function with poles at the negative integers.
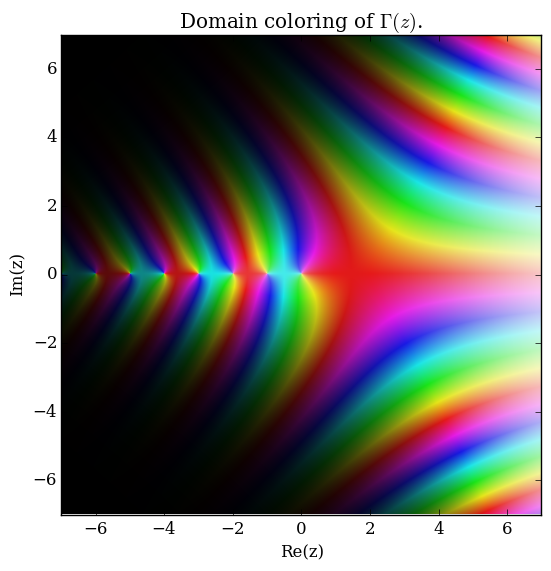
Domain coloring of $\Gamma$.
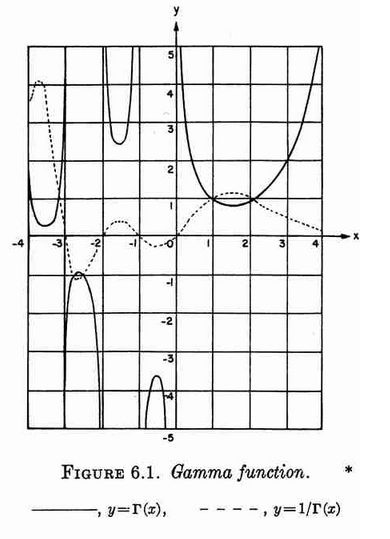
Plot of $\Gamma$ and $\dfrac{1}{\Gamma}$ from Abramowitz&Stegun.
Properties
Gamma(z) as integral of a power of log(1/t) for Re(z) greater than 0
Gamma function written as a limit of a factorial, exponential, and a rising factorial
Gamma function written as infinite product
Value of Gamma(1)
Factorial property of gamma
Gamma at positive integers
Relationship between Hurwitz zeta and gamma function
Gamma-Sine Relation
Bohr-Mollerup theorem
Gamma'(z)/Gamma(z)=-gamma-1/z+Sum z/(k(z+k))
Videos
What's the Gamma Function? (16 September 2008)
Gamma Function Of One-Half: Part 1 (10 August 2010)
Gamma Function Of One-Half: Part 2 (10 August 2010)
Gamma Integral Function - Introduction (5 December 2011)
gamma function - Part 1 (9 February 2012)
Gamma Function (playlist) (26 February 2012)
Gamma function (20 October 2012)
Beta Function, Gamma Function and their Properties (17 August 2013)
Thermodynamics 19 a : Gamma Function 1/2 (31 August 2013)
euler gamma function (14 September 2013)
The Gamma Function: intro (5) (13 February 2014)
The Gamma Function: why 0!=1 (5) (13 February 2014)
Mod-04 Lec-09 Analytic continuation and the gamma function (Part I) (3 June 2014)
Gamma function at 1/2 (3 January 2015)
Contour Integral Definition of the Gamma Function (18 January 2015)
External links
The sine product formula and the gamma function
Leonhard Euler's Integral: A Historical Profile of the Gamma Function
See Also
Loggamma
Polygamma
Reciprocal gamma
References
- 1895: Johann Heinrich Graf: Einleitung in die Theorie der Gammafunktion und der Euler'schen Integrale ... (previous) ... (next): $\S 3 (15_a)$
- 1920: Edmund Taylor Whittaker and George Neville Watson: A course of modern analysis ... (previous) ... (next): $\S 12 \cdot 1$
- 1953: Arthur Erdélyi, Wilhelm Magnus, Fritz Oberhettinger and Francesco G. Tricomi: Higher Transcendental Functions Volume I ... (next): $\S 1.1 (1)$
- 1956: Ian N. Sneddon: Special Functions of Mathematical Physics and Chemistry ... (previous) ... (next): $\S 5 (5.1)$
- 1960: Earl David Rainville: Special Functions ... (previous) ... (next): $15.(1)$
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): $6.1.1$
- 1969: Yudell L. Luke: The Special Functions And Their Approximations, Volume I ... (previous) ... (next) $2.1 (1)$