Difference between revisions of "Kelvin bei"
From specialfunctionswiki
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | =Properties= | ||
| + | |||
| + | =References= | ||
| + | * {{BookReference|Higher Transcendental Functions Volume II|1953|Arthur Erdélyi|author2=Wilhelm Magnus|author3=Fritz Oberhettinger|author4=Francesco G. Tricomi|prev=Kelvin ber|next=Kelvin ker}}: $\S 7.2.3 (19)$ | ||
{{:Kelvin functions footer}} | {{:Kelvin functions footer}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:SpecialFunction]] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:42, 4 March 2018
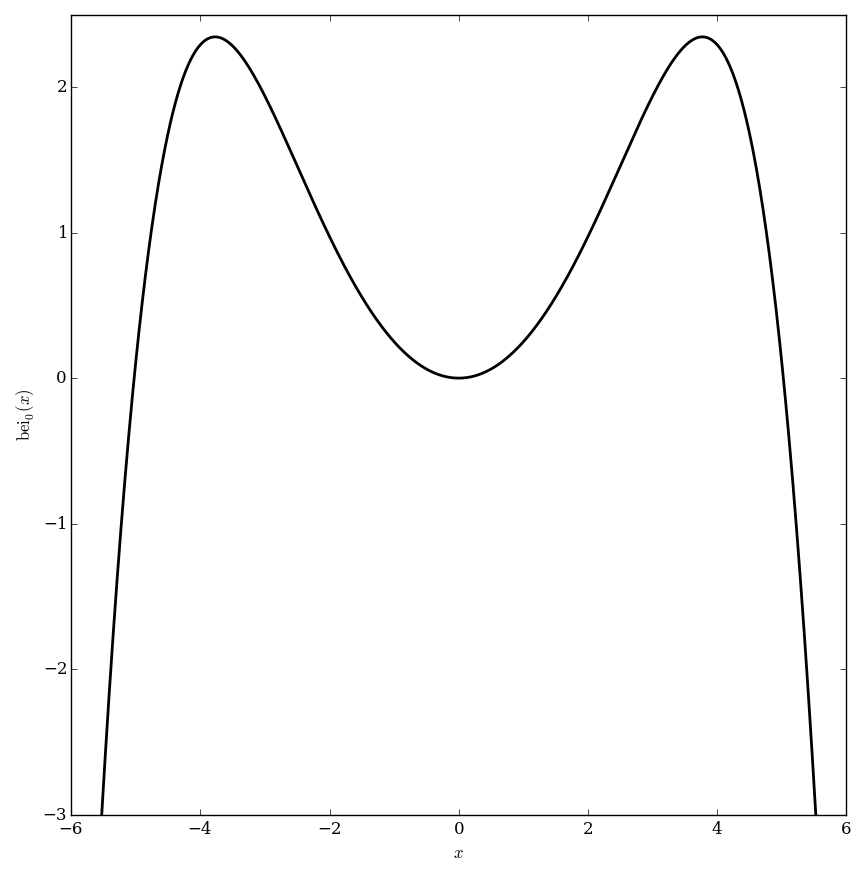
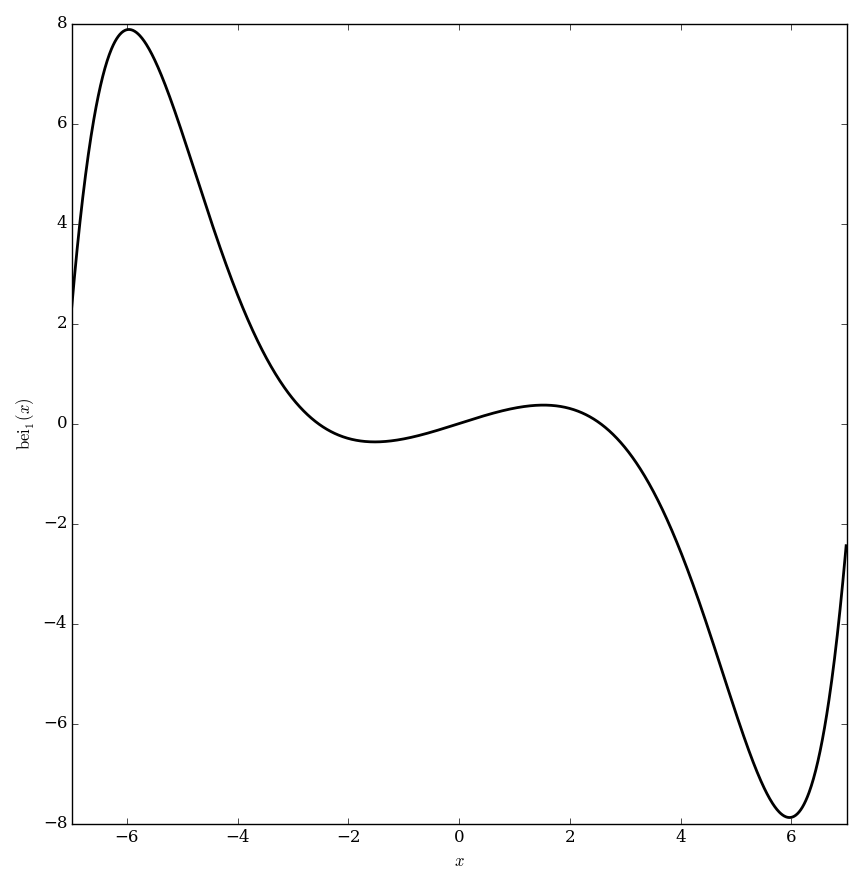
The $\mathrm{bei}_{\nu}$ function is defined as $$\mathrm{bei}_{\nu}(z)=\mathrm{Im} \hspace{2pt} J_{\nu} \left( z e^{\frac{3\pi i}{4}} \right),$$ where $\mathrm{Im}$ denotes the imaginary part of a complex number and $J_{\nu}$ denotes the Bessel function of the first kind.
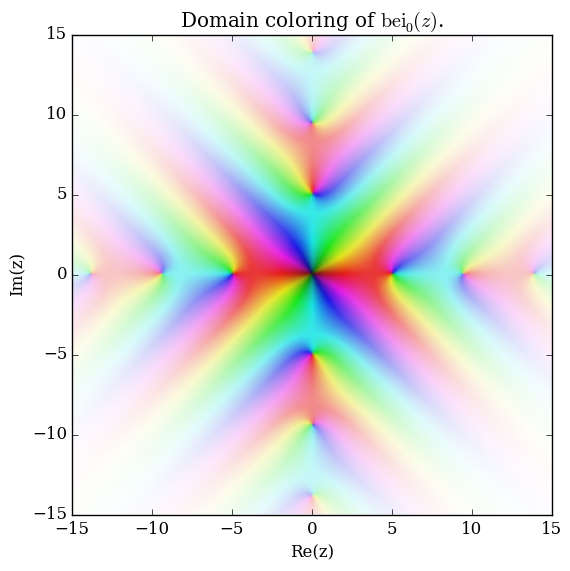
Domain coloring of $\mathrm{bei}_0$.
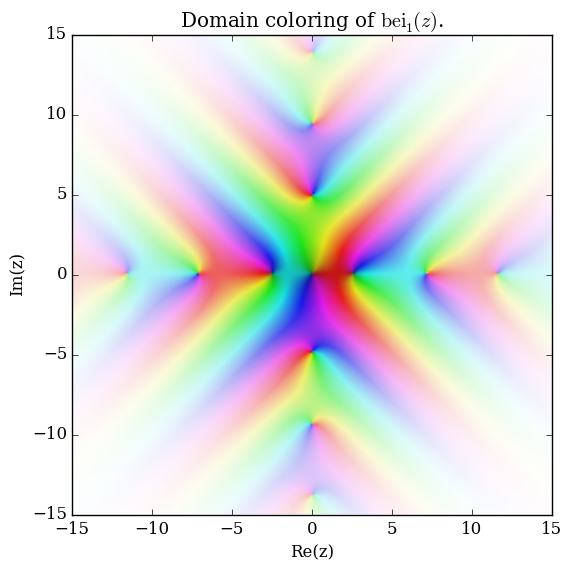
Domain coloring of $\mathrm{bei}_1$.
Properties
References
- 1953: Arthur Erdélyi, Wilhelm Magnus, Fritz Oberhettinger and Francesco G. Tricomi: Higher Transcendental Functions Volume II ... (previous) ... (next): $\S 7.2.3 (19)$