Difference between revisions of "Beta"
From specialfunctionswiki
(→Properties) |
(→Properties) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
=Properties= | =Properties= | ||
| − | + | {{:Beta in terms of gamma}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:800px"> | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:800px"> | ||
Revision as of 00:45, 21 March 2015
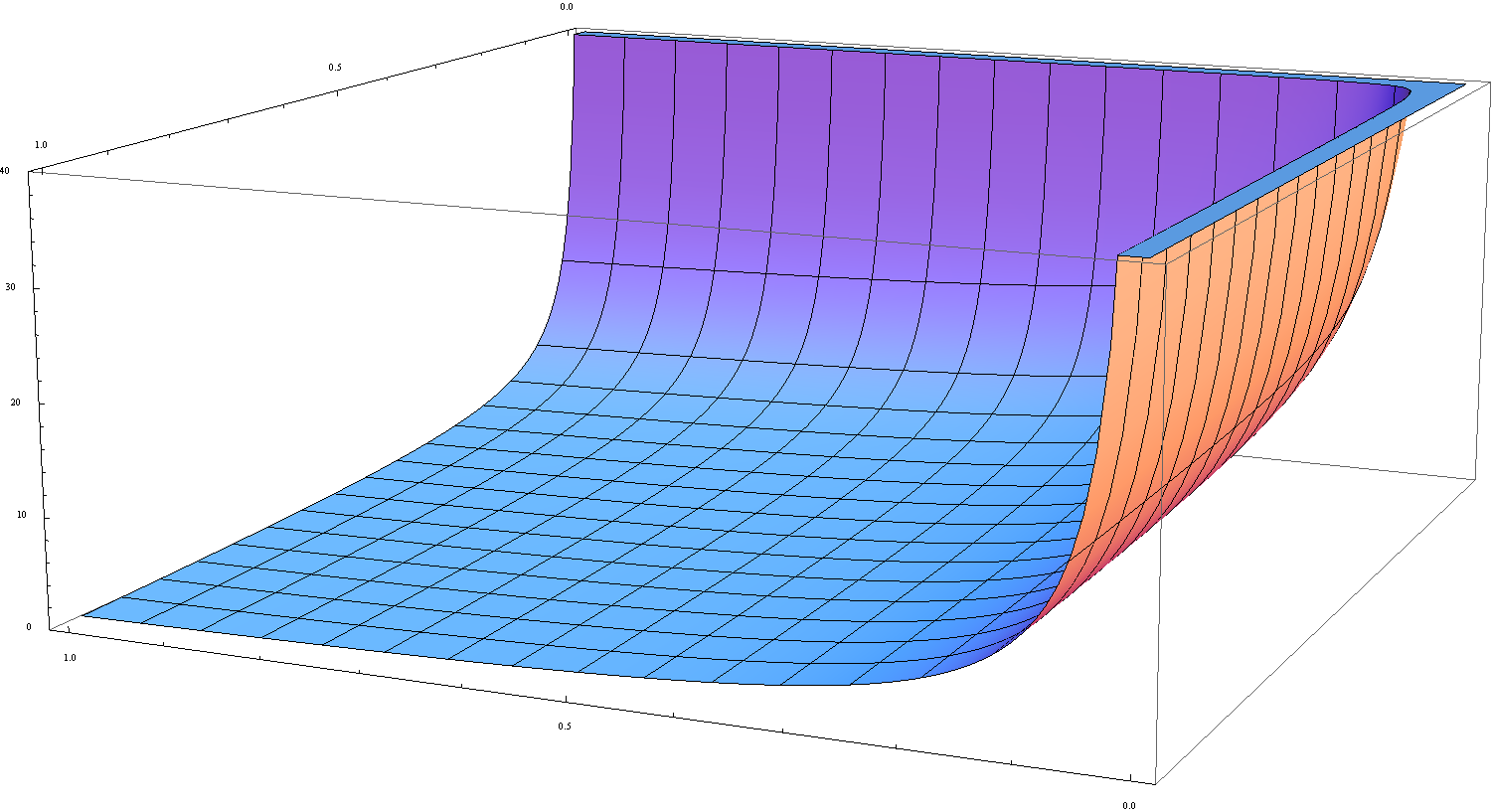
The $\beta$ function is defined by the formula $$B(x,y)=\displaystyle\int_0^1 t^{x-1}(1-t)^{y-1}dt.$$
Properties
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$B(x,y)=\dfrac{\Gamma(x)\Gamma(y)}{\Gamma(x+y)},$$ where $B$ denotes the beta function and $\Gamma$ denotes the gamma function.
Proof
References
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): $6.2.2$
Theorem: The following formula holds: $$B(x,y)=2 \displaystyle\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}} (\sin t)^{2x-1}(\cos t)^{2y-1}dt,$$ where $\sin$ and $\cos$ denote the sine and cosine functions.
Proof: █
Theorem: $B(x,y)=B(y,x)$
Proof: █
Theorem: (i) $B(x+1,y)=\dfrac{x}{x+y} B(x,y)$
(ii) $B(x,y+1)=\dfrac{y}{x+y}B(x,y)$
Proof: █
References
Bell. Special Functions
Special functions by Leon Hall