Difference between revisions of "Takagi function"
From specialfunctionswiki
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
[https://pure.ltu.se/ws/files/30923977/LTU-EX-03320-SE.pdf]<br /> | [https://pure.ltu.se/ws/files/30923977/LTU-EX-03320-SE.pdf]<br /> | ||
[http://www.math.tamu.edu/~tvogel/gallery/node7.html]<br /> | [http://www.math.tamu.edu/~tvogel/gallery/node7.html]<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:SpecialFunction]] | ||
Revision as of 18:35, 24 May 2016
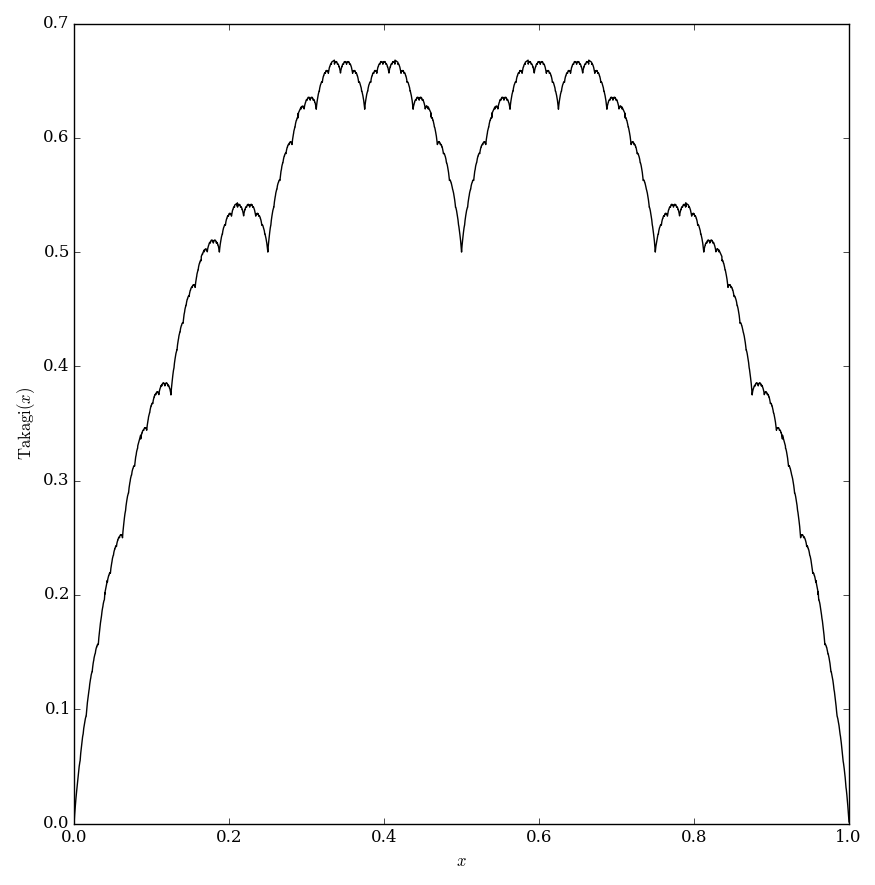
Define $s(x)=\inf_{n \in \mathbb{Z}} |x-n|$ (i.e. the distance from $x$ to the set of integers $\mathbb{Z}$). The Takagi function (also called the blancmange function) is defined by $$\mathrm{takagi}(x)=\displaystyle\sum_{k=0}^{\infty} \dfrac{s(2^n x)}{2^n}.$$ Note: to calculate $s(x)$ you may use $s(x)=\min \left(2^n x - \lfloor 2^n x \rfloor, \lceil 2^n x \rceil - x \right)$, where $\lfloor \cdot \rfloor$ denotes the floor function and $\lceil \cdot \rceil$ denotes the ceiling function.
Properties
Theorem: The Takagi function is continuous on $\mathbb{R}$.
Proof: █
Theorem: The Takagi function is nowhere differentiable on $\mathbb{R}$.
Proof: █