Difference between revisions of "Sine"
From specialfunctionswiki
(→References) |
|||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | * {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev= | + | * {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev=findme|next=Cosine}}: 4.3.1 |
[http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/mathematics/18-104-seminar-in-analysis-applications-to-number-theory-fall-2006/projects/chan.pdf The sine product formula and the gamma function] | [http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/mathematics/18-104-seminar-in-analysis-applications-to-number-theory-fall-2006/projects/chan.pdf The sine product formula and the gamma function] | ||
Revision as of 07:08, 8 June 2016
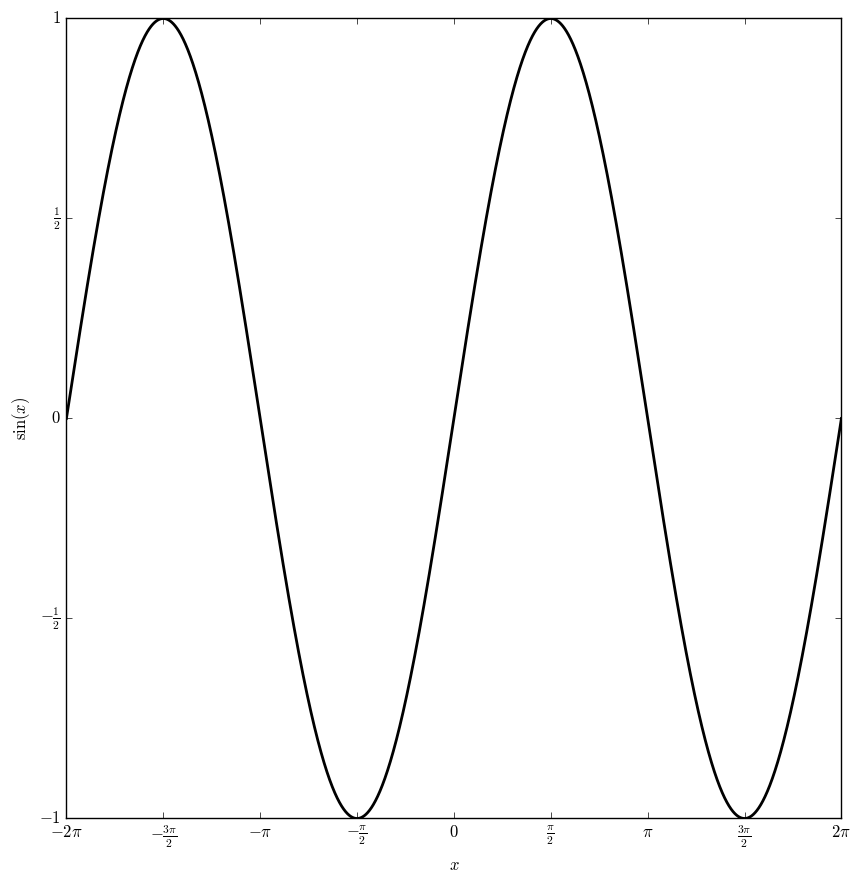
Definition
The sine function $\sin \colon \mathbb{C} \rightarrow \mathbb{C}$ is defined by $$\sin(z)=\dfrac{e^{iz}-e^{-iz}}{2i},$$ where $e^{iz}$ denotes the exponential function.
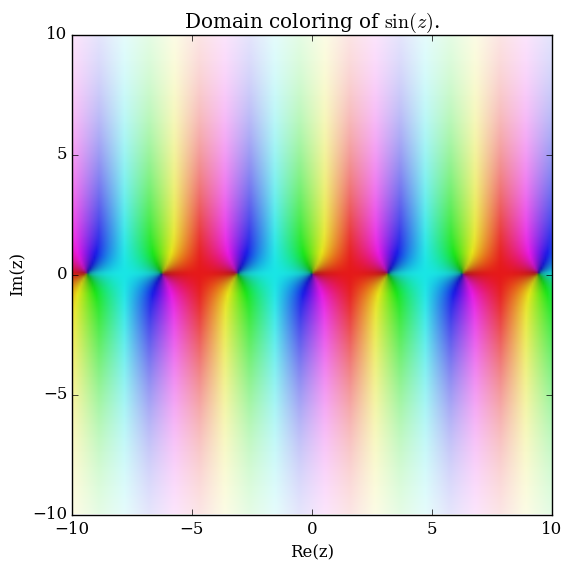
Domain coloring of $\sin$.
Properties
Derivative of sine
Pythagorean identity for sin and cos
Taylor series of sine
Weierstrass factorization of sine
Euler's reflection formula for gamma
Beta in terms of sine and cosine
Relationship between sine and hypergeometric 0F1
Relationship between spherical Bessel j sub nu and sine
Relationship between sin and sinh
Relationship between sinh and sin
Relationship between sine, Gudermannian, and tanh
Relationship between tanh, inverse Gudermannian, and sin
Videos
See Also
References
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): 4.3.1
The sine product formula and the gamma function