Difference between revisions of "Cosine"
From specialfunctionswiki
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | * {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev= | + | * {{BookReference|Handbook of mathematical functions|1964|Milton Abramowitz|author2=Irene A. Stegun|prev=Sine|next=Tangent}}: 4.3.2 |
<center>{{:Trigonometric functions footer}}</center> | <center>{{:Trigonometric functions footer}}</center> | ||
[[Category:SpecialFunction]] | [[Category:SpecialFunction]] | ||
Revision as of 07:09, 8 June 2016
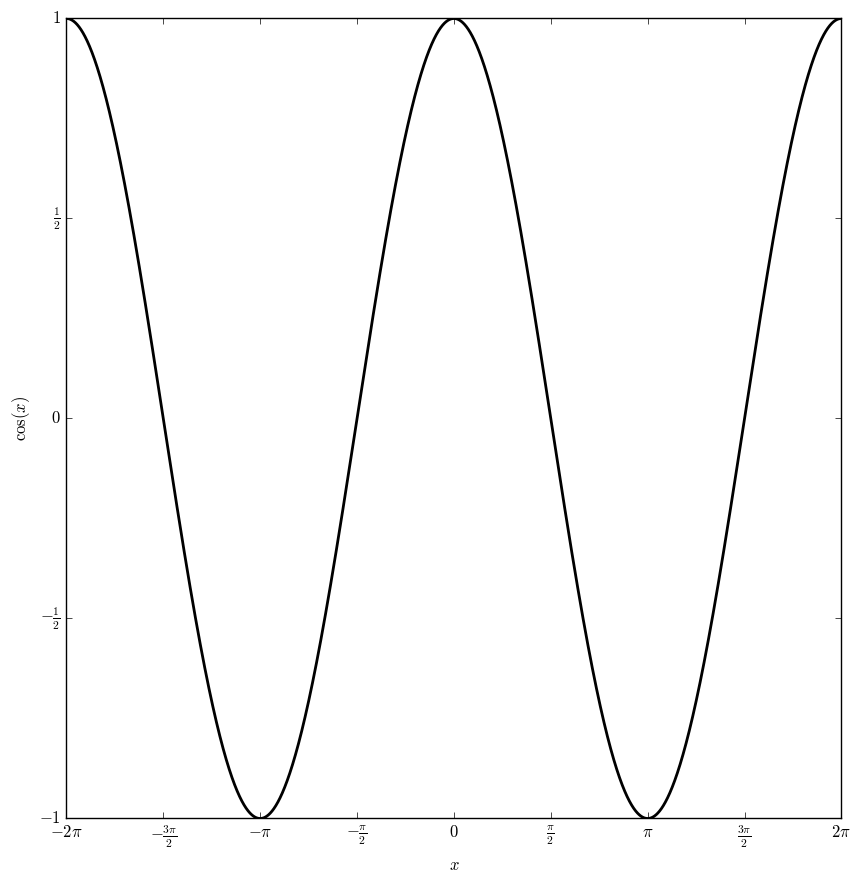
The cosine function, $\cos \colon \mathbb{C} \rightarrow \mathbb{C}$ is defined by the formula $$\cos(z)=\dfrac{e^{iz}+e^{-iz}}{2},$$ where $e^z$ is the exponential function.
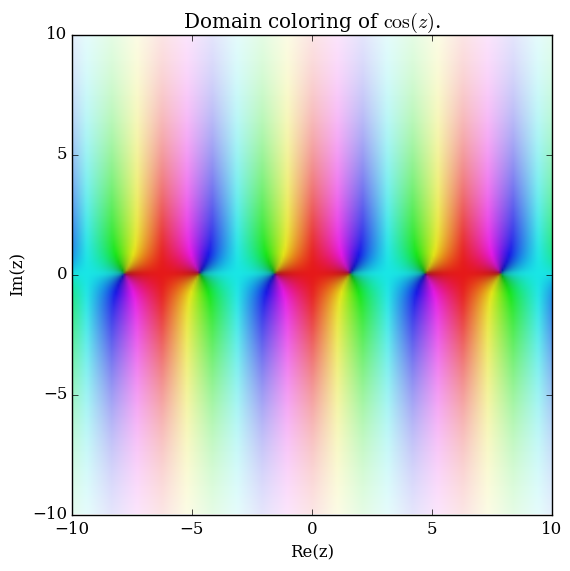
Domain coloring of $\cos$.
Properties
Derivative of cosine
Taylor series of cosine
Weierstrass factorization of cosine
Beta in terms of sine and cosine
Relationship between cosine and hypergeometric 0F1
Relationship between spherical Bessel y sub nu and cosine
Relationship between cosh and cos
Relationship between cos and cosh
Relationship between cosine, Gudermannian, and sech
Relationship between sech, inverse Gudermannian, and cos
See Also
References
- 1964: Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun: Handbook of mathematical functions ... (previous) ... (next): 4.3.2