Difference between revisions of "Laguerre L"
From specialfunctionswiki
(→Properties) |
|||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
[[L n'(0)=-n]]<br /> | [[L n'(0)=-n]]<br /> | ||
[[Orthogonality of Laguerre L]]<br /> | [[Orthogonality of Laguerre L]]<br /> | ||
| − | + | [[(n+1)L (n+1)(x) = (2n+1-x)L n(x)-nL (n-1)(x)]]<br /> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | </ | ||
<div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:800px"> | <div class="toccolours mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:800px"> | ||
Revision as of 14:30, 15 March 2018
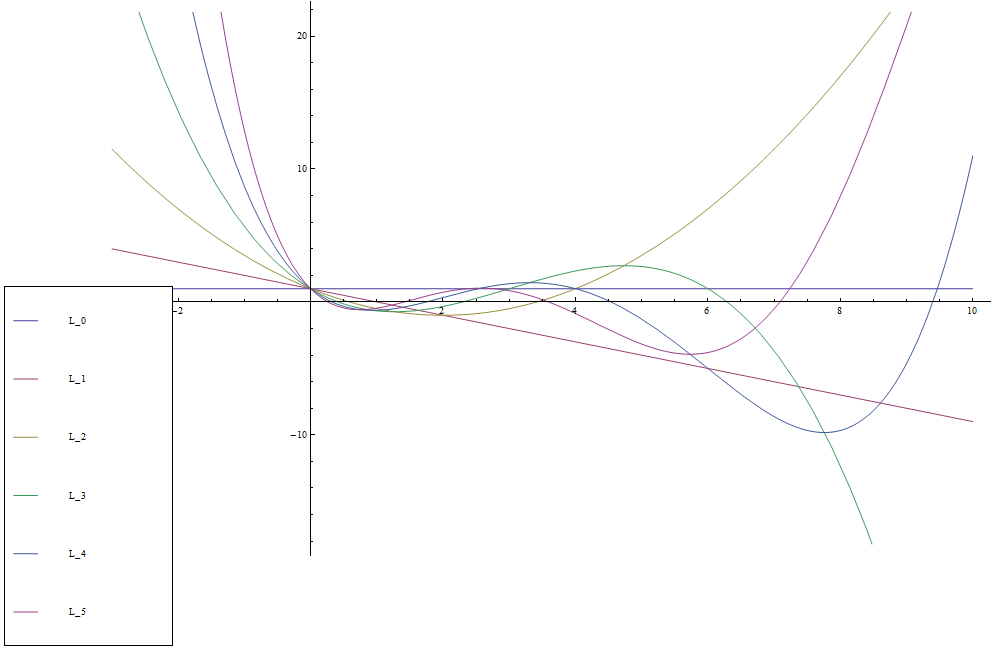
The Laguerre polynomial of order $n$, $L_n$, is given by $$L_n(x) = \displaystyle\sum_{k=0}^n \dfrac{(-1)^kn!}{(n-k)!(k!)^2}x^k.$$
The first few Laguerre polynomials are given by $$\begin{array}{ll} L_0(x) &= 1 \\ L_1(x) &= -x+1 \\ L_2(x) &= \dfrac{1}{2}(x^2-4x+2) \\ L_3(x) &= \dfrac{1}{6}(-x^3+9x^2-18x+6) \\ L_4(x) &= \dfrac{1}{24}(x^4-16x^3+72x^2-96x+24)\\ \vdots \end{array}$$
Properties
Generating function for Laguerre L
L n(x)=(e^x/n!)d^n/dx^n(x^n e^(-x))
L n(0)=1
L n'(0)=-n
Orthogonality of Laguerre L
(n+1)L (n+1)(x) = (2n+1-x)L n(x)-nL (n-1)(x)
Theorem: The following formula holds: $$xL_n'(x)=nL_n(x)-nL_{n-1}(x).$$
Proof: █
Theorem: The following formula holds: $$L_n'(x)=-\displaystyle\sum_{k=0}^{n-1} L_k(x).$$
Proof: █
See also
References
- 1968: W.W. Bell: Special Functions for Scientists and Engineers ... (previous) ... (next): $(6.3)$