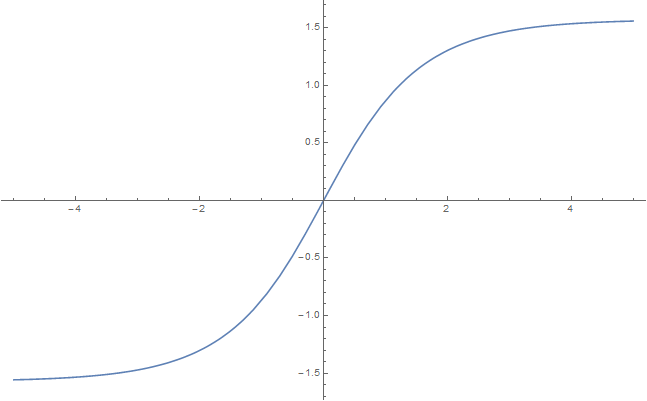
Gudermannian
The Gudermannian $\mathrm{gd}$ is defined for $x \in \mathbb{R}$ by the formula $$\mathrm{gd}(x) = \displaystyle\int_0^x \dfrac{1}{\cosh t} dt$$
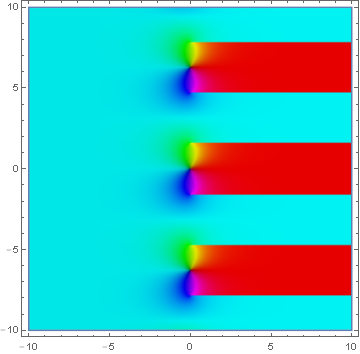
Domain coloring of $\mathrm{gd}$.
Contents
Properties
Theorem: The following formula holds: $\dfrac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d}x} \mathrm{gd}(x)=\mathrm{sech}(x).$
Proof: █
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\dfrac{\mathrm{gd}(x)}{2} = \displaystyle\sum_{k=0}^{\infty} \dfrac{(-1)^k \mathrm{tanh}^{2k+1}(\frac{x}{2})}{2k+1},$$ where $\mathrm{gd}$ is the Gudermannian and $\tanh$ is the hyperbolic tangent.
Proof
References
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\sin(\mathrm{gd}(x))=\tanh(x),$$ where $\sin$ denotes the sine, $\mathrm{gd}$ denotes the Gudermannian, and $\tanh$ denotes the hyperbolic tangent.
Proof
References
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\cos(\mathrm{gd}(x))=\mathrm{sech}(x),$$ where $\cos$ denotes the cosine, $\mathrm{gd}$ denotes the Gudermannian, and $\mathrm{sech}$ denotes the hyperbolic secant.
Proof
References
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\tan(\mathrm{gd}(x))=\sinh(x),$$ where $\tan$ denotes tangent, $\mathrm{gd}$ denotes the Gudermannian, and $\sinh$ denotes the hyperbolic sine.
Proof
References
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\csc(\mathrm{gd}(x))=\mathrm{coth}(x),$$ where $\csc$ is the cosecant, $\mathrm{gd}$ is the Gudermannian, and $\mathrm{coth}$ is the hyperbolic cotangent.
Proof
References
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\sec(\mathrm{gd}(x))=\cosh(x),$$ where $\sec$ denotes the secant, $\mathrm{gd}$ denotes the Gudermannian, and $\cosh$ denotes the hyperbolic cosine.
Proof
References
Theorem
The following formula holds: $$\cot(\mathrm{gd}(x))=\mathrm{csch}(x),$$ where $\cot$ is the cotangent, $\mathrm{gd}$ is the Gudermannian, and $\mathrm{csch}$ is the hyperbolic cosecant.
Proof
References