Difference between revisions of "Darboux function"
From specialfunctionswiki
(→Properties) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
where $\sin$ denotes the [[sine]] function. | where $\sin$ denotes the [[sine]] function. | ||
| − | + | <div align="center"> | |
| − | <div | + | <gallery> |
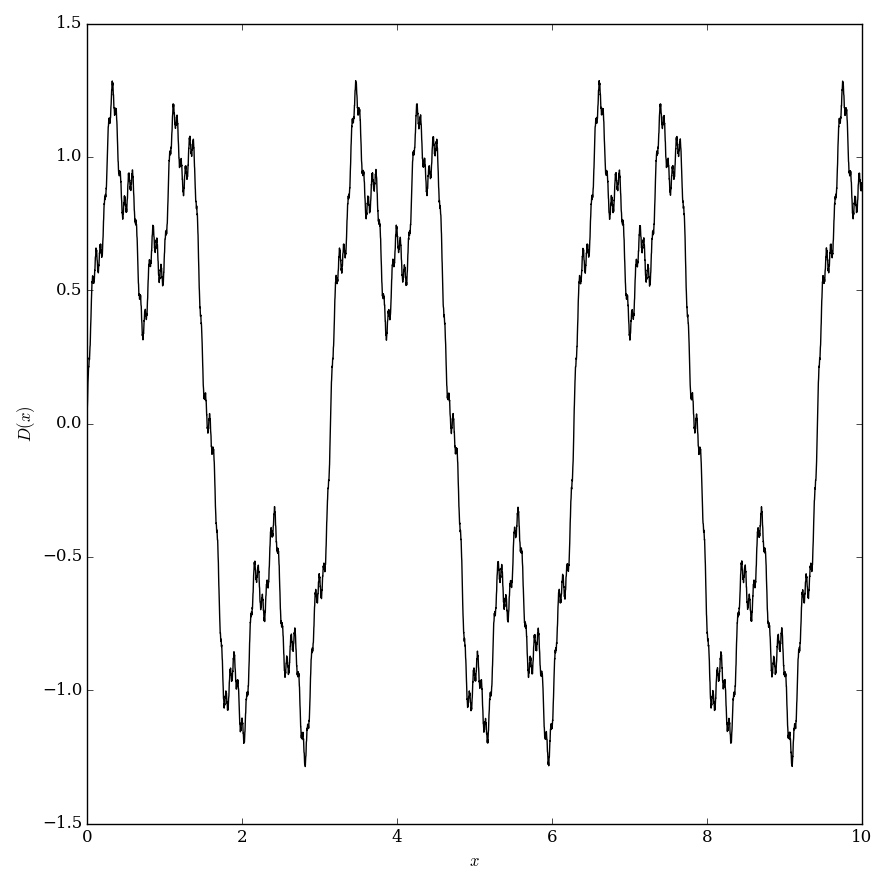
| − | < | + | File:Darbouxplot.png|Plot of $D(x)$ on $[0,5]$. |
| − | + | </gallery> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | + | =Properties= | |
| − | < | + | [[Darboux function is continuous]]<br /> |
| − | + | [[Darboux function is nowhere differentiable]]<br /> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | </ | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | [ | + | * {{BookReference|Continuous Nowhere Differentiable Functions|2003|Johan Thim|prev=findme|next=Schwarz function}} $\S 3.5$, pg. 28 |
| + | |||
| + | {{:Continuous nowhere differentiable functions footer}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:SpecialFunction]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:02, 25 June 2017
The Darboux function is defined by $$D(x)=\displaystyle\sum_{k=1}^{\infty} \dfrac{\sin\left((k+1)!x\right)}{k!},$$ where $\sin$ denotes the sine function.
Properties
Darboux function is continuous
Darboux function is nowhere differentiable
References
- 2003: Johan Thim: Continuous Nowhere Differentiable Functions ... (previous) ... (next) $\S 3.5$, pg. 28